Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-240716-13
- Publication
- Lu et al., 2024 - Localisation and function of key axonemal microtubule inner proteins and dynein docking complex members reveal extensive diversity among vertebrate motile cilia
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
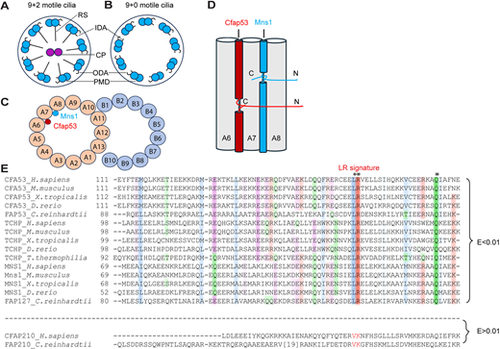
Motile cilia structure, CFAP53 and MNS1 protein disposition within the A tubule and their paralogous nature. (A,B) Diagram of (9+2) (A) and (9+0) motile cilia (B). The peripheral microtubule doublet (PMD), central pair (CP), inner dynein arm (ID), outer dynein arm (OD) and radial spoke (RS) are indicated. (C) Diagrammatic transverse section through the PMD, showing MNS1 and CFAP53 localisation within the A tubule. (D) Diagrammatic longitudinal section through the A tubule (microtubule protofilaments A6-A8), illustrating CFAP53 and MNS1 arrangement. C, C terminus; N, N terminus. (E) MSA of fMIP family members bearing the LRQ motif. Asterisks indicate invariably conserved residues. Proteins are designated by their UniProt identifiers. Colouring schemes are as per ClustalX parameters. Species represented are Homo sapiens, Mus musculus, Xenopus tropicalis, Danio rerio, Tetrahymena thermophilia and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. |