Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-230318-17
- Publication
- Kurolap et al., 2022 - Bi-allelic variants in neuronal cell adhesion molecule cause a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by developmental delay, hypotonia, neuropathy/spasticity
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
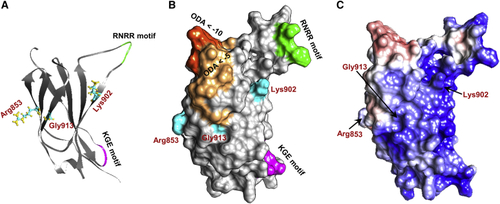
Structural modeling of the NRCAM third fibronectin type III (Fn-III) domain repeat The third Fn-III domain repeat contains a cluster of the variants identified in affected individuals, including three missense variants (p.Arg853Cys, p.Lys902Thr, and p.Gly913Asp) and two predicted loss-of-function variants (p.Arg929∗ and c.2647−2A>G). (A and B) Three-dimensional (3D) structure (A) and surface (B) of the Fn-III 3 domain. Residues involved in nonsynonymous changes—Arg853, Lys902, and Gly913—are depicted in cyan, and the domain’s KGE (magenta) and RNRR (green) motifs are highlighted. Optimal docking area (ODA) computation revealed regions predicted to belong to a protein-protein interface (dark orange represents ODA < −10 and light orange represents regions with ODA < −5). All three mutated residues are located either within or very close to the predicted ODA. Residue Lys902 is also located close to the domain’s KGE and RNRR motifs, which are important for protein-protein interactions. (C) Surface electrostatics analysis shows a clear electrostatic separation between negatively charged (red) and positively charged (blue) regions. The ODA depicted in (B) corresponds to the positively charged patch. |