Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-230318-16
- Publication
- Kurolap et al., 2022 - Bi-allelic variants in neuronal cell adhesion molecule cause a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by developmental delay, hypotonia, neuropathy/spasticity
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
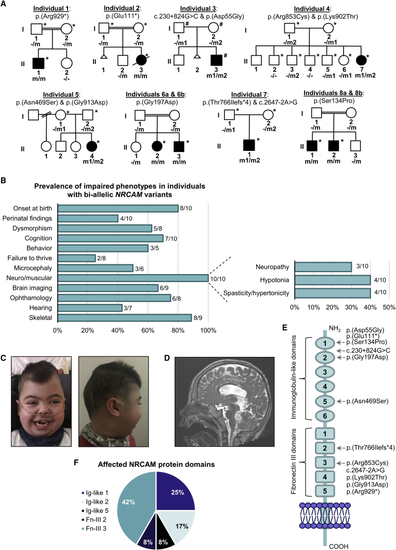
NRCAM variants in individuals with neurodevelopmental disease (A) Pedigrees and variant segregation in eight families with ten affected individuals harboring bi-allelic NRCAM variants; individuals that underwent whole-exome sequencing (∗) and whole-genome sequencing (#) are marked in each family. (B) Frequency of phenotypic features in individuals with bi-allelic NRCAM variants. (C) Facial dysmorphism of individual 1, including bi-temporal narrowing, bushy eyebrows with medial flaring, long eyelashes, depressed nasal bridge, and cupid bowed lips (left) and plagiocephaly (right). (D) Sagittal T2W imaging of individual 1’s brain reveals enlarged third and fourth ventricles and a thinned corpus callosum. The vermis is partially shifted off the midline yet not reduced in size. (E) Schematic representation of the NRCAM protein domains. The location of variants observed in individuals with NRCAM-related disease are highlighted. (F) Distribution of NRCAM variants among protein domains reveals a variant cluster in the third Fn-III domain repeat. |