FIGURE
Figure 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-210801-9
- Publication
- Li et al., 2021 - Disruption of MAP7D1 Gene Function Increases the Risk of Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiomyopathy and Heart Failure
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
Figure 4
|
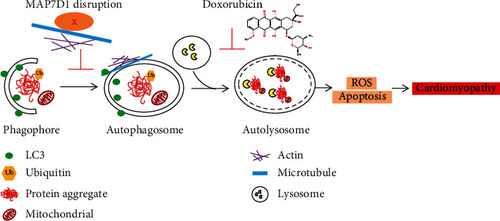
Working model of MAP7D1 in doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy. Doxorubicin causes cardiotoxicity by inhibiting autolysosome formation, resulting in elevated ROS and cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Disruption of MAP7D1 protein function further impaired autophagosome formation and led to accumulation of toxic protein aggregation, thus exacerbating doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy and heart failure. |
Expression Data
Expression Detail
Antibody Labeling
Phenotype Data
Phenotype Detail
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Biomed Res. Int.