|
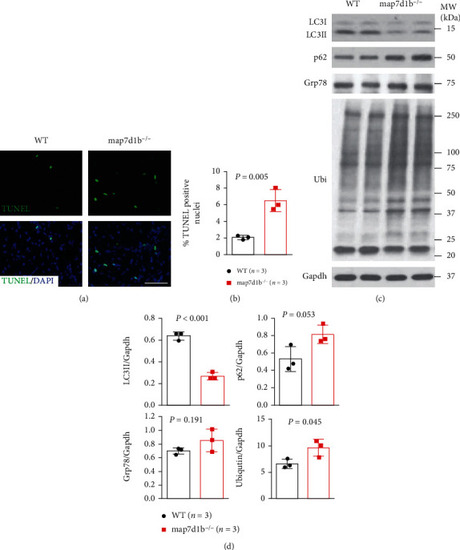
The GBT239/map7d1b homozygous mutant exhibited increased apoptotic cardiomyocyte death concurrent with impaired autophagy and elevated protein aggregation upon doxorubicin stress. (a, b) Representative images of the TUNEL assay (a) and quantification of the percentage of TUNEL-positive nuclei in GBT239/map7d1b homozygous mutant (map7d1b-/-) compared to WT controls at 4 weeks postdoxorubicin injection. n=4, Student’s t-test. Scale bar: 20 μm. (c, d) Representative Western blot images (c) and quantification analysis (d) of the expression levels of autophagy molecular markers LC3II and p62 (SQSTM1), ER stress marker glucose-regulated protein 78 (Grp78), and ubiquitin aggregated protein examined in the heart tissues isolated from the map7d1b-/- mutant compared to WT control at 4 weeks postdoxorubicin injection. n=3, Student’s t-test.
|