|
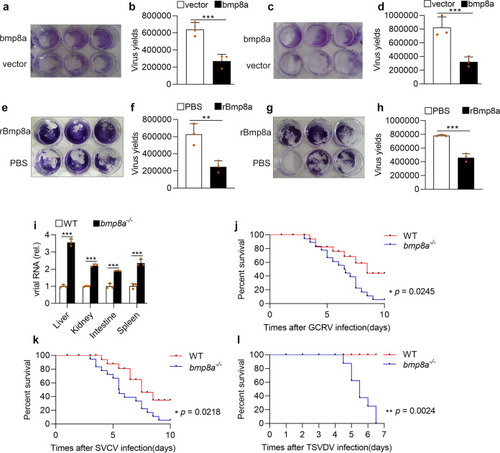
Bmp8a inhibits RNA virus replication both in vitro and in vivo.a, b ZFL cells were transfected with bmp8a (1 μg) or empty vector (1 μg), respectively. The cells were infected with GCRV (5 × 104 TCID50 per ml) at 24 h of post-transfection, and the culture supernatants were collected at 72 h of post-infection. The cell monolayers were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 1 h and stained with 0.5% crystal violet for 2 h (a), and the viral titers of the supernatants were determined by TCID50 assays (b). c, d Similar as (a, b) but in EPC cells. e, f ZFL cells were treated with rBmp8a (final concentrations of 5 μg/ml) or PBS co-incubation with GCRV (5 × 104 TCID50 per ml), and the culture supernatants were collected at 72 h of post-infection. The cell monolayers were fixed with 4% PFA for 1 h and stained with 0.5% crystal violet for 2 h (e), and the viral titers of the supernatants were determined by TCID50 assays (f). g, h Similar as (e, f) but in EPC cells. i The expression of GCRV RNA in the liver, kidney, intestine, and spleen from wild-type (WT) or bmp8a−/− zebrafish injected i.p. with 50 µl of GCRV (108TCID50 per ml) for 72 h. j, k Kaplan–Meier analysis of the overall survival of WT (n = 20) or bmp8a−/− zebrafish (n = 20) which were injected i.p. with 50 µl of GCRV (108TCID50 per ml) or SVCV (108TCID50 per ml) and monitored every 12 h after infection. l Kaplan–Meier analysis of the overall survival of WT (n = 8) or bmp8a−/− zebrafish (n = 8) which were injected i.p. with 50 µl of TSVDV (crude virus extracts filtered by a 0.45 μm microporous membrane) and monitored every 12 h after infection. The expression of zebrafish actb1 was used as an internal control for the qRT-PCR. Data were from three independent experiments (a–i) or two independent experiments (j–l). Data were analyzed by Student’s t-test (two-tailed) or log-rank (Mantel–Cox) test and were presented as mean ± SD (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001).
|