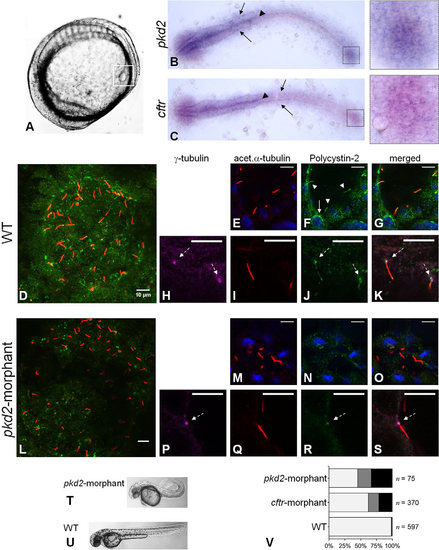
Polycystin-2 and CFTR expression. (A) Localization of KV (squared region) in the body of a 10–11s.s. zebrafish embryo. (B,C) RNA in situ hybridizations for pkd2 (B) and cftr (C) in 10–11s.s. WT embryos. Both pkd2 and cftr transcripts are detected in the KV region (right squares), neural floorplate (arrow heads), brain and pronephric ducts primordia (arrows). (D-S) Confocal images for the immunolocalization of Polycystin-2 in KV cells at the 10–11s.s. In WT embryos (D-K), Polycystin-2 is detected clustered near the nuclei (white arrow in F), along cilia (white arrow heads in F) and at the basal body (dashed arrows in H,J and K). In pkd2-morphants (L-S), the Polycystin-2 signal is markedly reduced and, although still detected at the basal body (dashed arrow in P,R and S), it is no longer detected along cilia. (D,L) maximal intensity z-stack projection; (E-K;M-S) z-section. Polycystin-2 (green), acetylated α-tubulin (red), γ-tubulin, (purple), nuclei (blue). Scale bars: 10µm. (T,U) Lateral view of pkd2-morphant (T) and WT (U) larvae at 72hpf. (V) Heart position defects: pkd2-morphants – 33% right-sided, 21% central; cftr-morphants – 21% right-sided, 17% central; and WT siblings – 0.7% right-sided, 1.0% central. Left-sided (light grey), central (dark grey) and right-sided hearts (black). n, number of scored embryos.
|

