|
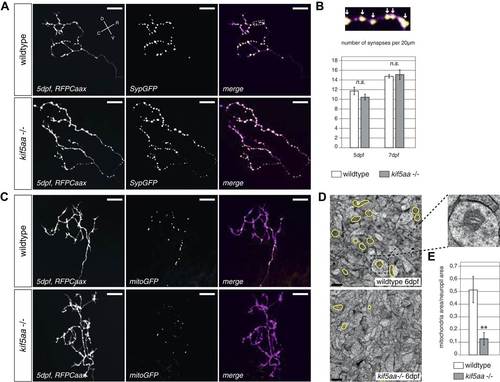
Kif5aa mutant RGC arbors show the same density of presynaptic sites but are depleted of mitochondria. (A) In vivo imaging shows the distribution of presynaptic sites marked by Synaptophysin-GFP (SypGFP) in single kif5aa mutant and wild-type RGC arbors expressing membrane localized RFP (RFPCaax). Upper panel: wild-type cell arbor, lower panel: kif5aa mutant cell arbor. Scale bars = 20 µm. D = dorsal, V = ventral, R = rostral, C = caudal. (B) Upper panel: Zoom in to an axonal segment indicated in the right panel of (A). Stable presynaptic clusters of SypGFP larger than 0.4 µm were defined as synapses (white arrows in the upper panel) and synapse density in axonal segments of wild-type and mutant cell arbors does not show a significant difference at 5 and 7 dpf (lower panel). (C) Distribution of mitochondria (labeled by mitoGFP) in single mutant and wild-type RGC arbors expressing membrane localized RFP (RFPCaax) in vivo. Upper panel: wild-type cell arbor, lower panel: kif5aa mutant cell arbor. Mutants RGC cell arbors show substantially less mitochondria. Scale bars = 20 µm. (D) Transmission electron micrograph of a transvers section of the neuropil containing RGC axonal arbors. Upper panel: wild-type neuropil, lower panel: kif5aa mutant neuropil. In yellow circles: mitochondria. Left panel: Zoom in into a single axonal segment containing a mitochondrion. The kif5aa mutant neuropil contains less mitochondria. Scale bar = 500 nm. (E) Quantification of mitochondria area per neuropil area comparing wild-type and mutant tecta at 6 dpf. Mutant cells contain significantly less mitochondria than wild-type cells (p < 0.01).
|