Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-140716-24
- Publication
- Duval et al., 2014 - gdf6a is required for cone photoreceptor subtype differentiation and for the actions of tbx2b in determining rod versus cone photoreceptor fate
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
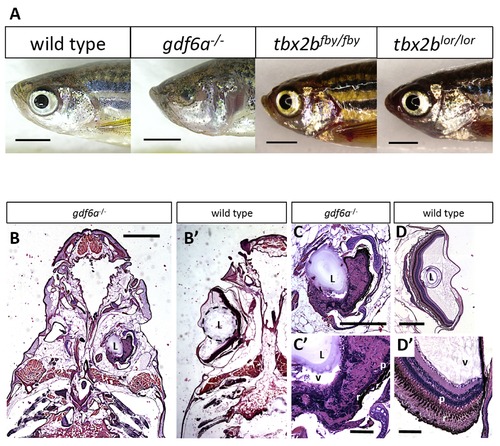
gdf6a and tbx2b mutants do not share the microphthalmic phenotype, despite a shared pathway in early eye development. A. gdf6as327/s327 mutants (labeled gdf6a/ in figures) exhibit microphthalmia to varying degrees of severity during development and throughout adulthood, unlike their wild type and heterozygous siblings. tbx2b mutants do not exhibit microphthalmia, and their eyes develop normally. Scale bars 2 mm. B, C, D. Coronal sections of adult zebrafish heads, comparing microphthalmic gdf6as327/s327 (B) and wildtype fish (B2). Microphthalmia and anophthalmia present variably in gdf6as327/s327 fish (e.g. right and left eyes in B, respectively) and eyes are often noted to possess a lens (L), though in this instance the right eye is inverted such that the anterior segment is oriented towards the midline. RPE (r) and a thin layer of photoreceptors (p) are discernable in gdf6as327/s327 fish (C2), though other retinal layers are not recognizable due to multiple tissue infoldings. In panel D, the lens was presumably displaced away from the iris during dissection/fixation. Note C is at higher magnification compared to D. Scale bar in B 1 mm; C, D is .5 mm; C2, D2 is .1 mm. L, lens; v, vitreous; r, RPE layer; p, photoreceptor layer. |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Adult |