Fig. 6
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-111028-17
- Publication
- Palencia-Desai et al., 2011 - Vascular endothelial and endocardial progenitors differentiate as cardiomyocytes in the absence of Etsrp/Etv2 function
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
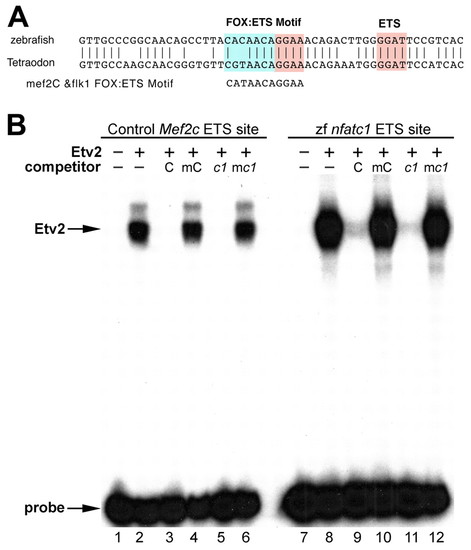
Zebrafish Nfatc1 promoter contains a conserved ETS-binding site that interacts with Etv2 protein in vitro. (A) Zebrafish and puffer fish Tetraodon nigroviridis share a conserved sequence within Nfatc1 promoter region that contains a Fox:Ets consensus site that is also present in multiple endothelial enhancers such as mef2c and flk1. The conserved sequences are located –13.9 kb and –5.4 kb from the translation start sites of zebrafish and Tetraodon Nfatc1, respectively. Pink and blue regions indicate consensus ETS and FOX binding sites, respectively. (B) Etv2 binds to the zebrafish nfatc1 site. Recombinant mouse Etv2 protein was used in EMSA with radiolabeled probes corresponding to a control ETS site from the mouse Mef2c gene (lanes 1-6) or to ETS site from the zebrafish nfatc1 gene (lanes 7-12). Lanes 1 and 7 contain unprogramed rabbit reticulocyte lysate without recombinant Etv2 protein. Etv2 bound efficiently to the control and nfatc1 ETS sites (lanes 2, 8). Binding to both sites was specifically competed by an excess of the wild-type unlabeled control (C) probe (lanes 3, 9) but not by an equivalent amount of a mutant version of the control probe (mC), which did not compete for binding to either probe (lanes 4, 10). Unlabeled zebrafish nfatc1 ETS probe (c1) also efficiently competed for binding to the control ETS site (lane 5) and to itself (lane 11). A mutant version of the nfatc1 ETS probe in which the ETS consensus was disrupted (mc1) did not compete for binding to either probe (lanes 6, 12). A plus sign indicates addition of lysate containing recombinant Etv2. A minus sign indicates lysate without recombinant Etv2 in the top row and indicates no addition of ETS site competitor in the lower row. |