FIGURE
Fig. s3
Fig. s3
|
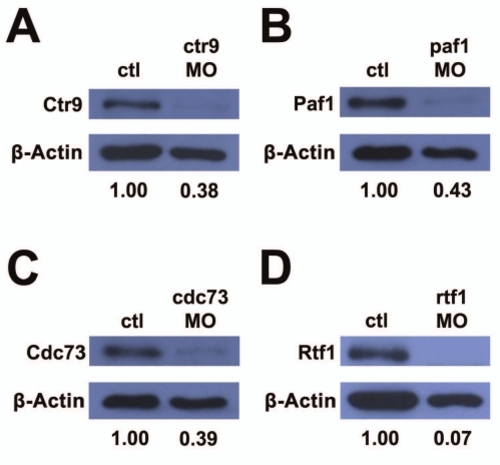
Morpholinos targeting PAF1C component genes reduce target protein levels. (A–D) Western blots detecting PAF1C component proteins and β-actin protein levels in uninjected control and morpholino injected embryo lysates. (A) Ctr9 protein is reduced to 38% of control levels in ctr9MO injected embryos. (B) Paf1 protein is reduced to 43% of control levels in paf1MO injected embryos. (C) Cdc73 protein is reduced to 39% of control levels in cdc73MO injected embryos. (D) Rtf1 protein is reduced to 7% of control levels in rtf1MO injected embryos. |
Expression Data
| Genes: | |
|---|---|
| Antibodies: | |
| Fish: | |
| Knockdown Reagents: | |
| Anatomical Term: | |
| Stage: | Prim-5 |
Expression Detail
Antibody Labeling
Phenotype Data
Phenotype Detail
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 353(1), Langenbacher, A.D., Nguyen, C.T., Cavanaugh, A.M., Huang, J., Lu, F., and Chen, J.N., The PAF1 complex differentially regulates cardiomyocyte specification, 19-28, Copyright (2011) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.