Fig. S1
|
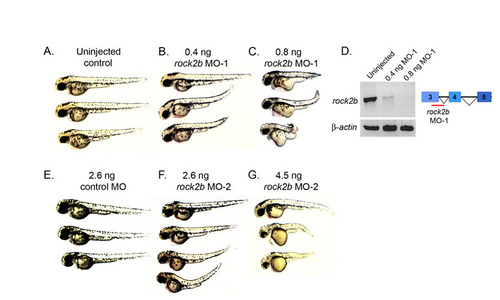
Dose-dependent rock2b MO knockdown phenotypes. (A-C) Live embryos at 2 dpf. A high dose (0.8 ng) of rock2b MO-1 caused severe axis elongation defects (C) relative to a low (0.4 ng) MO dose (B) and uninjected controls (A). (D) RT-PCR was used to determine efficacy of rock2b MO-1 that targets splicing of exons 3-4 of rock2b mRNA. The 0.4 ng MO dose resulted in a partial loss of spliced transcripts, whereas the 0.8 ng dose resulted in greater depletion. β-Actin was amplified as a control. rock2b exon-intron structure and the rock2b MO-1 target site are shown in the diagram in D. (E-G) Similar dose-dependent axis elongation defects were observed in rock2b MO-2 injected embryos at 2 dpf (F,G), relative to control MO injected embryos (E). |