Fig. 5
|
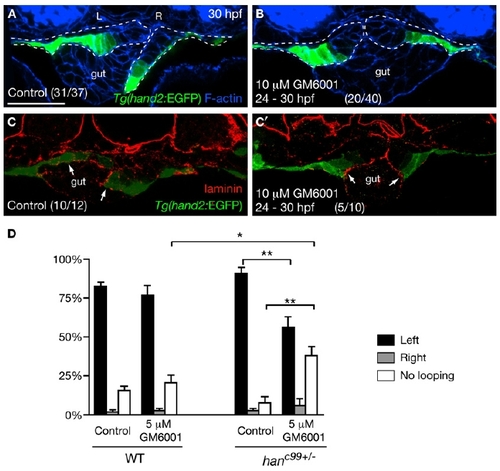
Asymmetric LPM Migration Requires the Diminishment of Laminin by MMPs (A and B) MMP inhibition blocked the asymmetric LPM migration. Tg(hand2:EGFP) embryos were treated with DMSO (A) or 10 μM GM6001 (B) from 24 hpf, and stained for GFP (green) and phalloidin (blue) at 30 hpf. Dashed lines outline the LPM. (C and C′) Laminin (red) deposition was diminished near the Tg(hand2:EGFP)-expressing cells in the DMSO-treated controls (C, arrows), but persisted along the entire LPM/gut boundary in GM6001-treated embryos (C′, arrows). (D) Proportions (mean ± SEM) of wild-type and hanc99+/- embryos showing gut-looping phenotypes according to foxa3 expression. Three independent experiments were conducted. Two hundred wild-type and 200 genotyped hanc99+/- embryos treated with DMSO or 5 μM GM6001 were examined. Asterisks indicate statistical significance: *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. (A–C′) Transverse sections, dorsal to the top. L, left; R, right. The scale bar represents 40 μm. See also Figure S2. |
| Antibody: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Condition: | |
| Anatomical Term: | |
| Stage: | Prim-15 |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Condition: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Prim-15 |
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 18(6), Yin, C., Kikuchi, K., Hochgreb, T., Poss, K.D., and Stainier, D.Y., Hand2 Regulates Extracellular Matrix Remodeling Essential for Gut-Looping Morphogenesis in Zebrafish, 973-984, Copyright (2010) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell