|
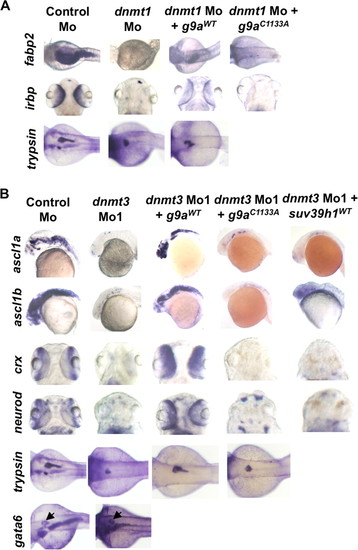
G9a overexpression rescues both dnmt3 morphants and dnmt1 morphants. Whole mount in situ analysis of ascl1a, ascl1b, crx, and neurod (A) and fabp2, irbp, and trypsin (B) expression in embryos injected with control morpholino or dnmt3 or dnmt1 morpholino co-injected with wild-type or catalytically null G9a or Suv39h1. ascl1a and ascl1b were analyzed at 30 hpf, whereas all others were analyzed at 80 hpf. Note that co-injection of wild-type G9a (G9aWT) but not of either catalytically inactive G9a (G9aC1133S) or wild-type Suv39h1 rescues the ascl1a and ascl1b expression in dnmt3 morphants. Overexpression of wild-type G9a, but not catalytically inactive G9a, can also rescue fabp2 and irbp expression in dnmt1 morphants. Of note, wild-type G9a could not rescue trypsin expression in dnmt1 morphants. The panel showing Suv39h1 rescue of dnmt1 morphants has been reported previously (7) and is shown for comparative purposes.
|