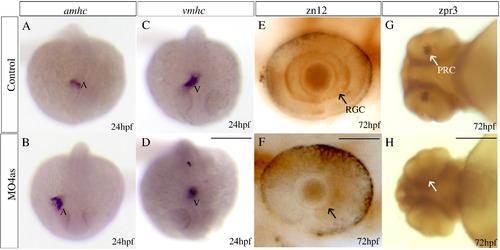
irx4a is involved in cardiac chamber specification and retinal development. Control and irx4a morphant embryos were processed for in situ hybridization (A–D) or immunohistochemistry (E–H). (A–D) Morphant embryos (B, D) show an increase in the size of the atrium and a decrease in the size of the ventricle compared to control embryos (A, C) as revealed the expression of the amhc (A, B) and vmhc (C, D) markers, respectively. (E, F) zn12 immunostaining labels retinal ganglion cells (RGC) in control embryos (E, arrow) but they are not detected in MO4as injected embryos (F). (G, H) zpr-3 immunostaining labels photoreceptor cells (PRC) in the 72 hpf control larva (G, arrow) but not in the morphant larva (H); note that photoreceptors have only differentiated in the ventral retina at this stage. A–D, dorsal views of whole embryos at 24 hpf, anterior is down; E, F, lateral views of the eye at 72 hpf, anterior is left; G, H, ventral views of the head. Scale bar in D: 40 μm for A–D, scale bar in F: 7 μm for E, F; scale bar in H: 15 μm for G, H.
|

