- Title
-
Zebrafish CCNF and FUS Mediate Stress-Specific Motor Responses
- Authors
- Aksoy, Y.A., Cole, A.J., Deng, W., Hesselson, D.
- Source
- Full text @ Cells
|
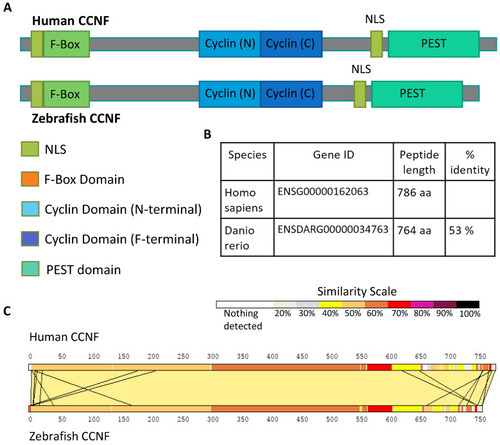
Schematic overview of CCNF protein. ( |
|
Generating |
|
Schematic overview of FUS protein. ( |
|
Generating |
|
Motor neuron axon growth and length. The average length of six motor neurons above the yolk sac extension were analysed in all three genotypes of ( |
|
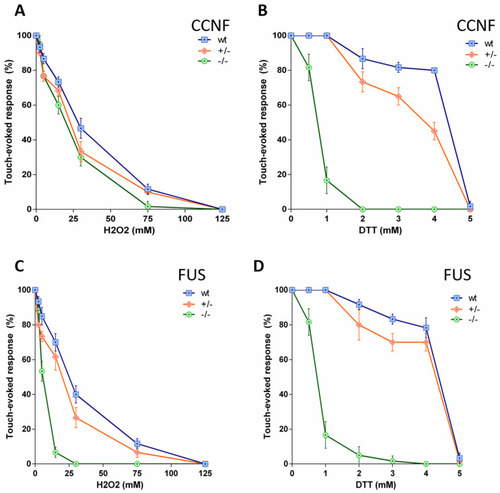
Touch-evoked response of 2dpf zebrafish larvae treated with H2O2 and DTT. ( |
|
Photomotor response of |