- Title
-
Efficacy of Jiuzao polysaccharides in ameliorating alcoholic fatty liver disease and modulating gut microbiota
- Authors
- Li, Q., Pei, R., Chen, E., Zheng, F., Zhang, Y., Meng, S.
- Source
- Full text @ Heliyon
|
Experimental design for zebrafish larvae. |
|
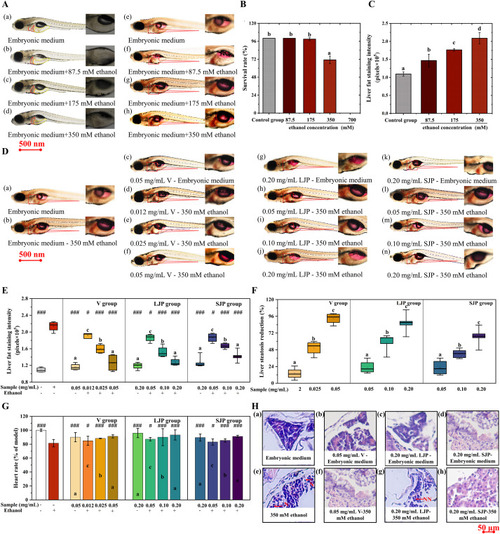
Micrograph snapshots (a–d) and comprehensive whole-mount Oil red O staining images (e–h) of zebrafish larvae liver across varied ethanol gradients (A). Denotations: L-hepatic zone; Y-yolk sac area. A circumscribed liver, enhanced for visual clarity, delineates lipid droplet accumulation utilized in steatosis scoring. Survival rates of zebrafish larvae across ethanol concentration gradients (B). Grayscale intensity quantifications of larval liver exposed to varying ethanol gradients (C). Representative imagery of whole-mount Oil red O staining in zebrafish larvae (D), alongside hepatic fat staining intensities (E), reduction in hepatic steatosis (F), cardiac rate metrics (G). Analyses were conducted using ImageJ software. Prototypical histopathological snapshots of zebrafish larval livers (H) with annotations: NN-normative nucleus; NP-nuclear peripheral alignment; V-vacuolation; K-karyolysis. Data represented as mean ± SD. Significance markers: #<0.05, ##<0.01, ###<0.001 when compared against the model group, evaluated via student's t-test. Different lowercase letters denote significant differences. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.) |
|
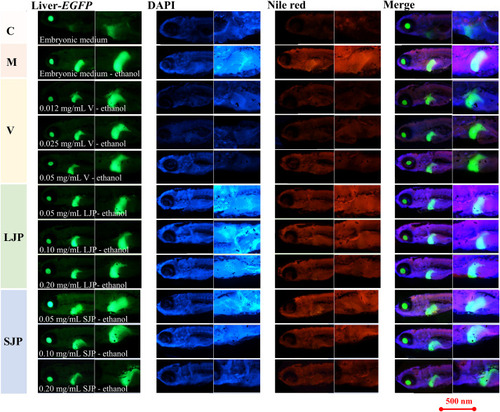
Illustration of Nile red staining. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.) |
|
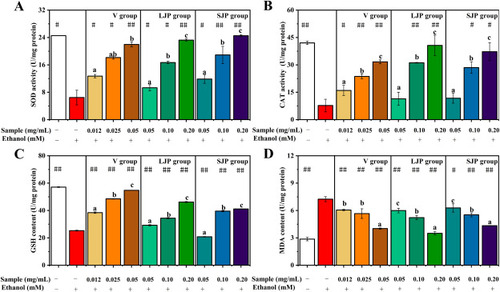
Influence of Jiuzao polysaccharides on enzymatic activities in alcoholic fatty liver-afflicted zebrafish larvae. (A) SOD. (B) CAT. (C) GSH. (D) MDA. Data presented as mean ± SD. #<0.05, ##<0.01, ###<0.001 compared to the model group, analyzed via student's t-test. Different lowercase letters denote significant differences. |
|
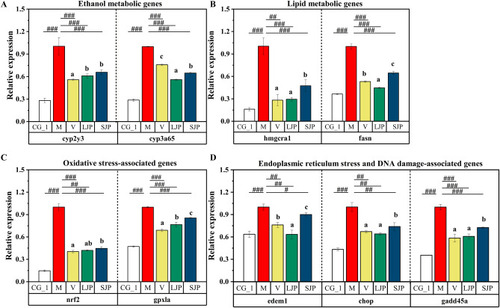
Jiuzao polysaccharides mitigate ethanol-induced disturbances and lipid metabolism, reduce oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress, and counteract DNA damage in zebrafish larvae. RT-qPCR elucidated the expression patterns of ethanol metabolism-associated genes, cyp2y3 and cyp3a65 (A). RT-qPCR depicted lipid metabolism-associated genes, hmgcra and fasn (B). RT-qPCR of oxidative stress markers, nrf2 and gpxla, was carried out (C). The expression of endoplasmic reticulum stress and DNA damage-associated genes, edem1, chop, and gadd45αa, were assessed (D). Data are expressed as mean ± SD. #<0.05, ##<0.01, ###<0.001 denote significance against the model group as determined by the student's t-test. Different lowercase letters denote significant differences. |
|
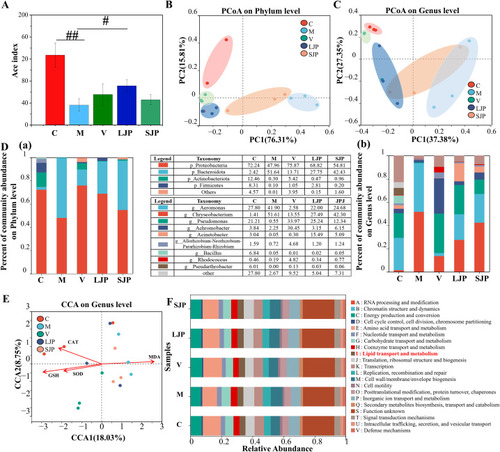
Alleviation of ethanol-induced gut dysbiosis by Jiuzao polysaccharides. Genus-level Ace index (A). Phylum-level PCoA (B). Genus-level PCoA (C). Relative abundance histograms of gut microbial phyla and genera (D (a and b)). Genus-level RDA (E). COG functional classification (F). #<0.05 and ##<0.01 versus the model group employing student's t-test. |