- Title
-
Cebp1 and Cebpβ transcriptional axis controls eosinophilopoiesis in zebrafish
- Authors
- Li, G., Sun, Y., Kwok, I., Yang, L., Wen, W., Huang, P., Wu, M., Li, J., Huang, Z., Liu, Z., He, S., Peng, W., Bei, J.X., Ginhoux, F., Ng, L.G., Zhang, Y.
- Source
- Full text @ Nat. Commun.
|
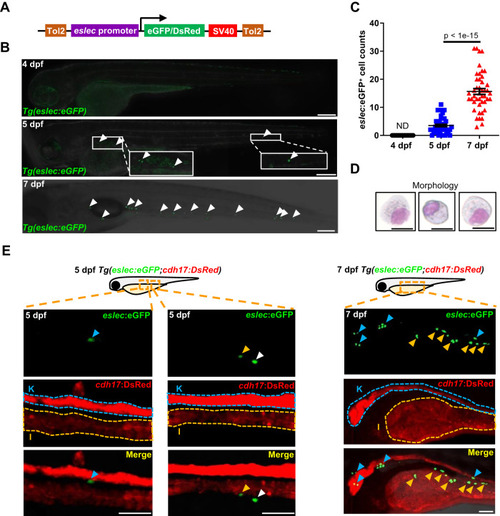
The early spatial-temporal development and function of zebrafish eosinophils. |
|
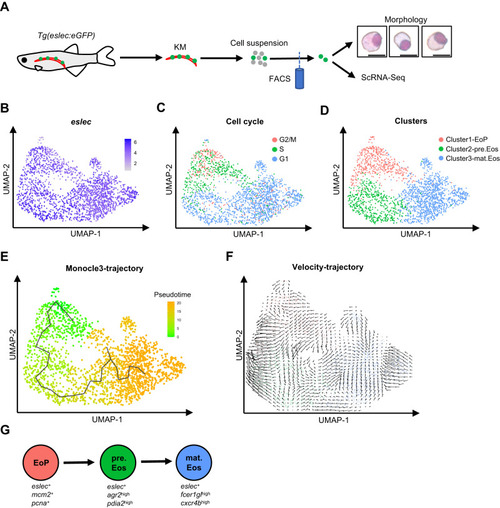
Landscape of the eosinophilic cell lineage. |
|
Cebp1 inhibits the commitment of eosinophils. |
|
|
|
Cebpβ promotes the commitment of the eosinophil lineage. |
|
Cebpβ promotes eosinophilopoiesis by regulating pre.Eos-related genes. |
|
Cebp1 is the orthologue of human C/EBPεP27 in suppressing eosinophilopoiesis. |
|
The working model showing zebrafish Cebps in balancing granulopoiesis. HSC or myeloid progenitor (MP) undergo stepwised differentiation for granulopoiesis. The neutrophil lineage cells contain proNeu1, proNeu2, pre.Neu, and mat.Neu, which nomenclature is based on a previous study |