- Title
-
Cooperative contributions of the klf1 and klf17 genes in zebrafish primitive erythropoiesis
- Authors
- Suzuki, H., Ogawa, T., Fujita, S., Sone, R., Kawahara, A.
- Source
- Full text @ Sci. Rep.
|
The PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Primitive myelopoiesis in the EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Blood circulation in wild-type and |
|
Wright–Giemsa staining of erythroid cells from wild-type and |
|
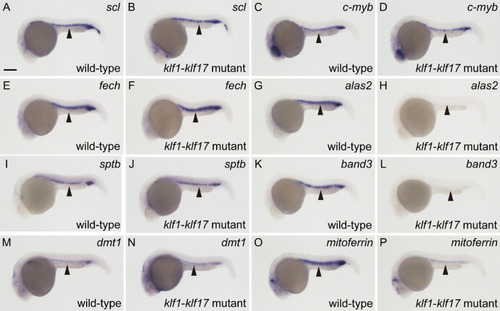
Differential expression of haematopoietic genes in the |
|
Expression levels of haematopoietic genes in the |