- Title
-
Regular Supplementation with Antioxidants Rescues Doxorubicin-Induced Bone Deformities and Mineralization Delay in Zebrafish
- Authors
- Poudel, S., Martins, G., Cancela, M.L., Gavaia, P.J.
- Source
- Full text @ Nutrients
|
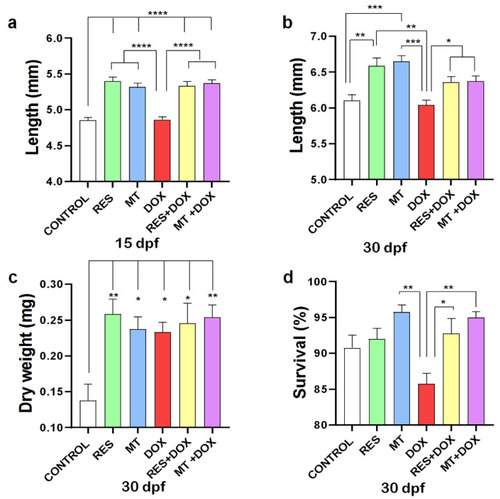
Growth and survival. Larvae were fed with resveratrol (RES), MitoTEMPO (MT) and doxorubicin (DOX) alone or in combination for 30 days. Total length of zebrafish larvae at 15 days post fertilization (dpf) (N = 25 × 4) ( PHENOTYPE:
|
|
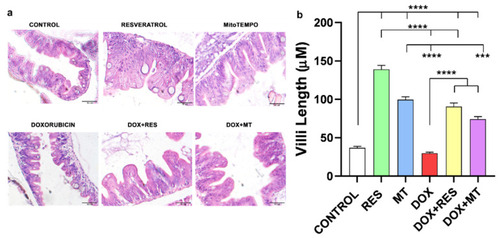
Histology of zebrafish gut. Total of 30 dpf zebrafish guts sections was stained with H&E to observe the villi from the different treatment groups with resveratrol (RES), MitoTEMPO (MT) and doxorubicin (DOX) ( |
|
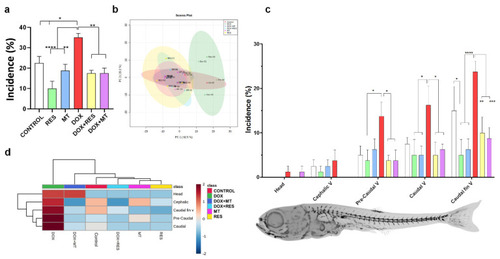
Incidence and distribution of skeletal deformities. Incidence of skeletal deformities ( |
|
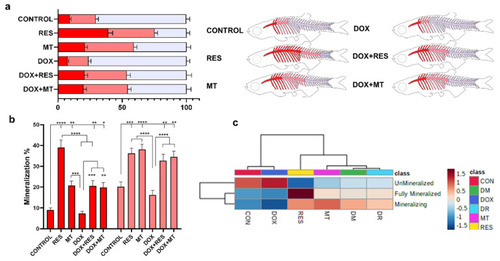
Mineralization of zebrafish vertebral column. Percentage of mineralized (red), mineralizing (pink), unmineralized (blue) vertebrae ( PHENOTYPE:
|
|
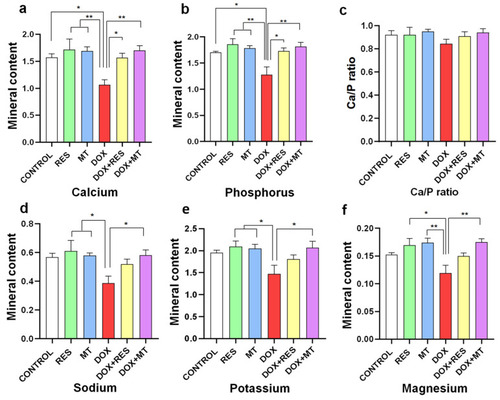
Mineral analysis of zebrafish fed with microdiets supplemented with antioxidants, resveratrol (RES) and MitoTEMPO (MT), and pro-oxidant, doxorubicin (DOX). Mineral content of Calcium ( PHENOTYPE:
|
|
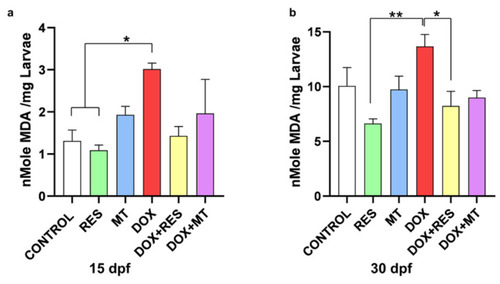
Lipid peroxidation on zebrafish fed microdiets enriched with antioxidants, resveratrol (RES) and MitoTEMPO (MT), and pro-oxidant, doxorubicin (DOX). Lipid peroxidation of the zebrafish larvae at 15 dpf ( PHENOTYPE:
|
|
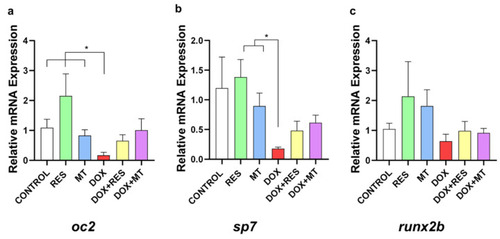
Doxorubicin affects osteoblastic markers. mRNA expression of osteoblast differentiation markers on zebrafish fed with resveratrol (RES), MitoTEMPO (MT) and doxorubicin (DOX) supplemented microdiets, alone or in combination; |