- Title
-
Different inflammation responses modulate Müller glia proliferation in the acute or chronically damaged zebrafish retina
- Authors
- Iribarne, M., Hyde, D.R.
- Source
- Full text @ Front Cell Dev Biol
|
Acute and chronic damaged retinas induce microglia activation and Müller glia proliferation. At 3 wpf, undamaged |
|
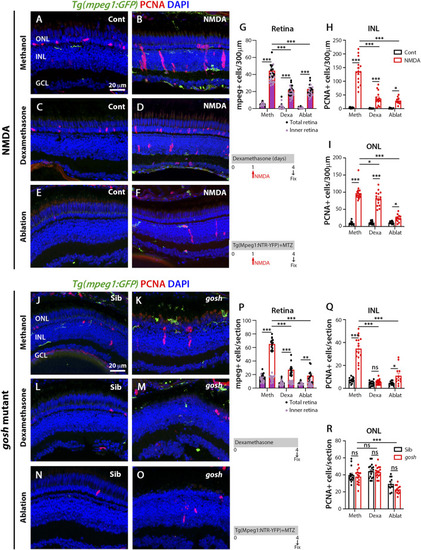
Suppressing microglia affect Müller glia proliferation in NMDA-injured retina and |
|
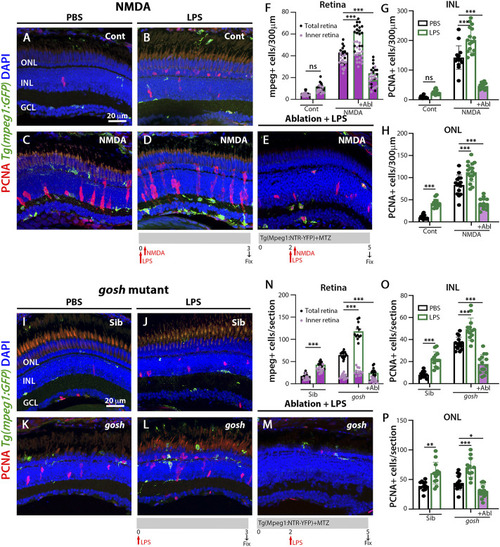
LPS-activated microglia enhance Müller glia proliferation in NMDA-injured retina and |
|
The acute injury model induces pro-inflammatory cytokine gene expressions that switch to anti-inflammatory cytokine expressions, whereas chronic injury shows the simultaneous expression of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory gene expressions. Quantitative real-time PCR was used to determine the fold-change of mRNA expressions of |
|
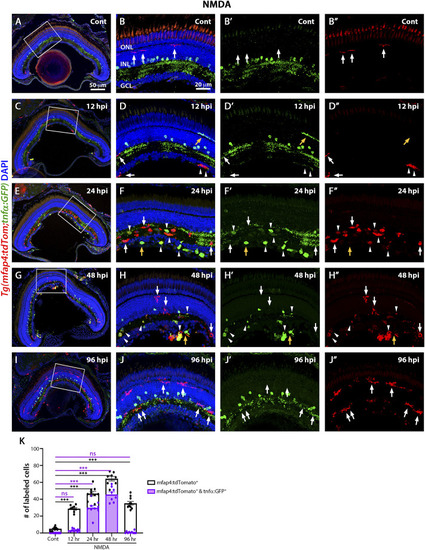
M1-like pro-inflammatory microglia are transiently identified in the NMDA-damaged acute injury model. Double-transgenic fish |
|
The |
|
M1-like microglia are modulated by dexamethasone and LPS treatment in acute and chronic damaged retinas. At 3 wpf, |
|
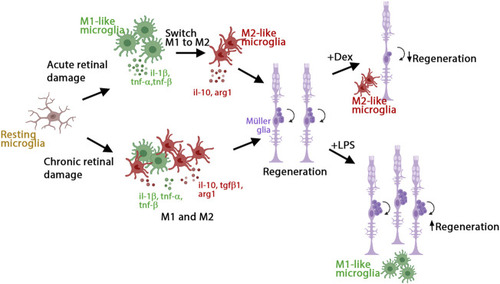
Model of inflammation regulating the regenerative response in acute and chronic retinal damage in zebrafish. Diagram representing microglia/macrophages activation and polarization upon NMDA-acute injury or |