- Title
-
Posterior axis formation requires Dlx5/Dlx6 expression at the neural plate border
- Authors
- Narboux-Neme, N., Ekker, M., Levi, G., Heude, E.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS One
|
Early phenotype of Dlx5/6-inactivated zebrafish and mouse. (A-B) Phenotype of wild type (WT) and dlx5a/6a morphant zebrafish at 48 hpf (n>750 for each condition). (C-D) Phenotype of WT and Dlx5/6-/- mutant mice at E11.5 (n = 6 for each condition). Inactivation of Dlx5/6 in zebrafish and mouse leads to early defect of posterior axis development characterized by curly-shaped tail phenotype in both models (B, D, white arrowheads). In Dlx5/6-/- embryos, the caudal phenotype is associated with defect of brain formation (D, blue arrowhead). Scale bar in B for A-B 100 μm, for C-D 1000 μm. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Dorsal midline defects in perinatal Dlx5/6-/- mice. (A-D) Macroscopic dorsal view (A-B) and skeletal preparation (C-D) of the posterior axis of control Dlx5/6+/- and Dlx5/6-/- mutant mice at E18.5 (n = 6 for each condition). (E-F) Immunostaining on coronal cryosections for Tnnt3 in dorsal musculature of control Dlx5/6+/- and Dlx5/6-/- E18.5 foetuses (n = 3 for each condition). Dlx5/6-/- mutants display a dorsal split already evident at macroscopic inspection (B, red arrowheads). This phenotype is associated with defects of thoracic/lumbar vertebrae (D, red arrowhead) and of epaxial muscle formation at the dorsal midline (F, red arrowheads). Abbreviations: em, epaxial muscles. Scale bars in B and D 2000 μm and in E 200 μm |
|
Dlx5 expression analysis during zebrafish and mouse posterior neurulation. (A-D) Whole-mount in situ hybridization for dlx5a and Dlx5; (A, C) dorsal and (B, D) lateral views of the posterior axis of 15.5 hpf and 16 hpf zebrafish (A-B) and E8.25 and E9.5 mouse embryos (C-D). (E-H) In situhybridization for Dlx5 on coronal cryosections at the levels indicated by the dashed lines in (C, D and S1 Fig). In zebrafish embryos, dlx5a transcripts are detected in NPB cells along neural keel at 15.5 hpf and at the dorsal midline at 16 hpf (A-B, black arrowheads). During mouse posterior neurulation, Dlx5 is expressed in NPB cells surrounding the posterior neuropore and along the dorsal midline of the neural tube after neural tube closure (C-H, black arrowheads). In both species, Dlx5 is also detected in the ventral ectodermal ridge of the tail bud and at the cloacal level (grey and blue arrowheads respectively in B, D) (n>10 for each conditions). Abbreviations: nc, notochord; nk, neural keel; np, neural plate; nt, neural tube; pnp, posterior neuropore; psm, presomitic mesoderm; sm, somitic mesoderm; tb, tail bud; ys, yolk sac. Scale bar in H for A, H 50 μm, for B, E-G 75 μm, for C 150 μm, for D 200 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Altered posterior neurulation in early dlx5a/6a zebrafish morphants. (A-H) Dorsal views of whole-mount in situ hybridization for ncad, ncam3, msx1b and foxd3 in controls (injected with water) and dlx5a/6a morphants at 16 hpf (n>8 for each condition). (A’-H’) In situ hybridization for ncad, ncam3, msx1b and foxd3 on coronal cryosections of 16 hpf controls and dlx5a/6a morphants at levels indicated by lines in (A, H). During neural keel-rod transition, the dlx5a/6a morphants show a decrease or loss of ncad, ncam3 and msx1b in aberrant protruding foxd3-positive NCC at the dorsal midline of the neural keel (black arrowhead in B’-H’). The morphants also present a delay in neural keel-rod transition characterized by bifid stripes of expression caudally (F-H, grey arrowheads). Abbreviations: nc, notochord; ncc, neural crest cells; nk, neural keel; psm, presomitic mesoderm; sm; somitic mesoderm. Scale bar in H for A-H 100 μm, for A’-H’ 25 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Defects of neural tube and motoneuron formation in dlx5a/6a zebrafish morphants. (A-F) Lateral views of whole-mount in situ hybridization for foxd3, ncad and msx1b in controls and dlx5a/6a zebrafish morphants at 24 hpf (n>8 for each condition). (A’-D’) In situ hybridization for foxd3 and ncad on coronal cryosections at levels indicated by lines in (A-D). The dlx5a/6a morphants show a reduced neural tube (A’-D’) associated with a defect of NCC migration (B’, black arrowhead), aberrant accumulation of foxd3 and ncadtranscripts in somites (B, D) and decrease of msx1b in the neural tube (F, black arrowhead). (G-L) Lateral views of whole-mount immunostaining for SV2 in 24 hpf, 30 hpf and 36 hpf control and dlx5a/6a morphant embryos (n>8 for each condition). In dlx5a/6a morphants at 24 hpf and 30 hpf, axonal projections of primary motoneurons fail to form (H-J). In 36 hpf morphants, primary motoneurons show abnormal synaptic connections to their myotomal targets (L). Abbreviations: mff, median fin fold; my, myotomes; nc, notochord; ncc, neural crest cells; nt, neural tube; pmn, primary motoneurons; psm, presomitic mesoderm; sm; somitic mesoderm, ys, yolk sac. Scale bar in A for A-F 100 μm, for A’-D’ 25 μm and for G-L 50 μm. |
|
(A, B) Lateral views of whole-mount in situ hybridization for Dlx5 in E10.5 and E12.5 mice. The dashed lines indicate the section levels analysed in Fig 3G and 3H. Dlx5 expression is detected at the cloacal level and in the VER at E10.5 (A, blue and grey arrowheads respectively) but is not detectable at E12.5. Abbreviations: nt, neural tube; sm, somitic mesoderm; tb, tail bud; ver, ventral ectodermal ridge. Scale bar in A for A-B 200 μm. |
|
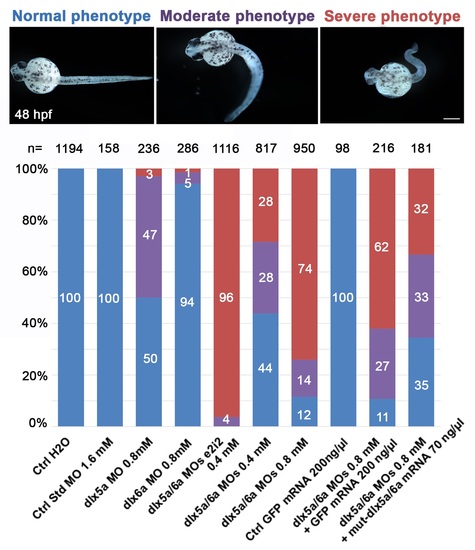
Proportion of normal (blue), moderate (purple) and severe (red) phenotypes observed at 48 hpf after morpholino knockdown and mRNA rescue experiments. The number (n) of specimens analysed is indicated for each treatment. Treatments: control embryos injected with H2O; control embryos injected with a control standard MO (1.6 mM); single morphants injected with either dlx5a or dlx6a translation-blocking MOs (0.8 mM); double morphants co-injected with dlx5a and dlx6a e2i2 splice-blocking MOs (0.4 mM each); double morphants co-injected with dlx5a and dlx6a translation-blocking MOs at two different concentrations (0.4 mM or 0.8 mM each); control embryos injected with GFP mRNA (200 ng/μl); embryos co-injected with dlx5a/6a translation-blocking MOs (0.8 mM each) and GFP mRNA (200 ng/μl) and embryos co-injected with dlx5a/6a translation-blocking MOs (0.8 mM each) and mutated dlx5a/dlx6a mRNAs (70 ng/μl each). Scale bar 100 μm. |
|
(A-H) Lateral views of whole-mount in situ hybridization in controls (injected with water) and dlx5a/6a zebrafish morphants for fgf8a at 16 hpf (A-B), shha at 24 hpf and 48 hpf (C-F) and for bmp4 at 48 hpf (G-H) (n>8 for each condition). The inactivation of dlx5a/6aleads to defects of somite boundaries as highlighted by fgf8a expression in the anterior somitic mesoderm at 16 hpf (A-B). Expression of shha in the notochord and neural tube floor plate well reveals the ondulating axis phenotype observed in dlx5a/6a morphants (C-F). At 48 hpf, the axis malformation is associated with a decrease of bmp4 expression in the spinal cord (G-H). Abbreviations: cn, chordoneural hinge; fp, floor plate; mff, median fin fold; my, myotomes; nc, notochord; nt, neural tube; sm, somites; sp, spinal cord. Scale bar in G for A-B 75 μm, for C-H 100 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|