- Title
-
HHEX is a transcriptional regulator of the VEGFC/FLT4/PROX1 signaling axis during vascular development
- Authors
- Gauvrit, S., Villasenor, A., Strilic, B., Kitchen, P., Collins, M.M., Marín-Juez, R., Guenther, S., Maischein, H.M., Fukuda, N., Canham, M.A., Brickman, J.M., Bogue, C.W., Jayaraman, P.S., Stainier, D.Y.R.
- Source
- Full text @ Nat. Commun.
|
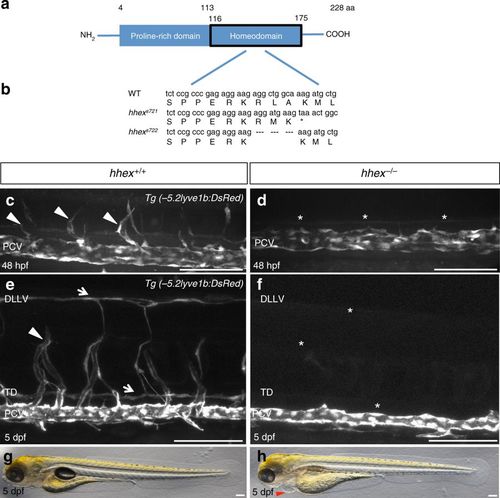
Zebrafish hhex mutants lack sprouting angiogenesis from the posterior cardinal vein. a Schematic representation of Hhex. Hhex, 228 amino acids (aa) long, is composed of a proline-rich domain (4–113 aa) and a homeodomain (116–175 aa). b Alignment of partial Hhex homeodomain sequence in wild-type (WT), and two mutant alleles, hhexs721 and hhexs722. The hhexs721 allele contains a 10 bp insertion leading to a premature stop codon within the homeodomain coding region, whereas the hhexs722 allele lacks amino acids R149 to A151. c, d Trunk vasculature of Tg(−5.2lyve1b:DsRed); hhex+/+ and hhex−/− embryos at 48 hpf. hhex mutant trunks exhibit a defect in sprouting angiogenesis from the posterior cardinal vein (PCV) (arrowheads point to tip cells sprouting from the PCV; asterisks indicate lack of tip cells sprouting from the PCV). e, f Trunk vasculature of Tg(−5.2lyve1b:DsRed); hhex+/+ and hhex−/− larvae at 5 dpf. hhex mutant trunks exhibit a defect in the formation of the venous intersegmental vessels (vISVs), the thoracic duct (TD) lymphatic vessel, and the dorsal longitudinal lymphatic vessel (DLLV) (arrowhead points to a vISV; arrows point to the ventrally positioned TD and dorsally positioned DLLV; asterisks indicate lack of these structures). g, h Brightfield lateral views of hhex+/+ and hhex−/− larvae at 5 dpf. Mutant larvae exhibit pericardial edema (arrowhead). Scale bars: 100 μm |
|
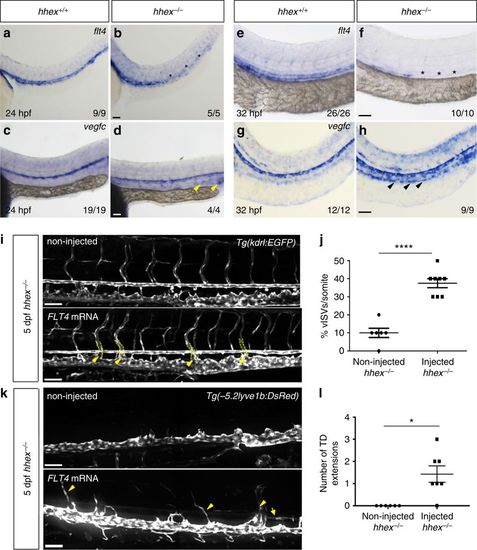
The Vegfc/Flt4 pathway is affected in zebrafish hhex mutants. a–d Whole-mount in situ hybridization showing flt4 (a, b) and vegfc (c, d) expression in 24 hpf hhex+/+ and hhex−/− embryos. At 24 hpf, hhex mutants exhibit decreased flt4 expression (asterisks), whereas vegfc expression in the PCV appears to be slightly increased (arrowheads). e–h Whole-mount in situ hybridization showing flt4 (e, f) and vegfc (g, h) expression at 32 hpf in hhex+/+ and hhex−/− embryos. At 32 hpf, hhex mutants exhibit a strong decrease in flt4 expression (asterisks), whereas vegfc expression is clearly increased in the PCV (arrowheads). x/y: number of embryos showing representative phenotype (x), number of embryos examined (y). i Trunk vasculature of 5 dpf Tg(kdrl:EGFP); hhex−/− injected, or not, with full-length human FLT4 mRNA. hhex mutants exhibit partial rescue of their vISVs at 5 dpf (arrowheads point to vISVs). j Quantification of vISVs across 10 somites in 5 dpf non-injected hhex−/− (n = 6) and FLT4 mRNA-injected hhex−/− (n = 8). k Trunk lymphatic vasculature of 5 dpf Tg(−5.2lyve1b:DsRed); hhex−/− injected, or not, with full-length human FLT4 mRNA. hhex mutants exhibit partial rescue of their TD at 5 dpf (arrowheads point to vISVs and arrow points to TD). l Quantification of TD extensions across 10 somites in 5 dpf non-injected hhex−/− (n = 6) and FLT4 mRNA-injected hhex−/− (n = 7). Values represent means ± s.e.m. ****P ≤ 0.0001 and *P ≤ 0.05 by t-test. Scale bars: 50 μm |
|
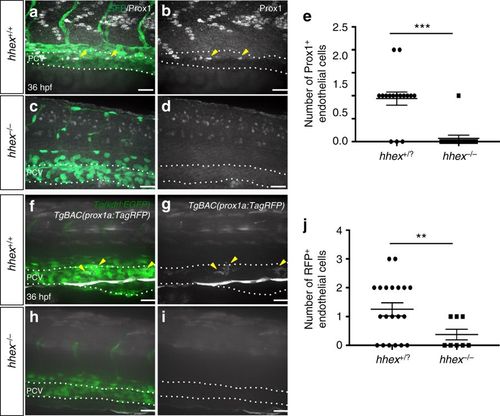
Zebrafish hhex mutants lack lymphatic precursors. a–d Whole-mount views of 36 hpf hhex+/+ and hhex−/− embryos immunostained for Prox1 (arrowheads point to Prox1+ endothelial cells in the PCV). e Quantification of the number of Prox1+ endothelial cells across three somites (from two field of view per embryo) in hhex+/? (n = 8) and hhex−/− (n = 6). f–i Whole-mount views of 36 hpf Tg(prox1a:TagRFP); hhex+/+ and hhex−/− embryos. hhex mutants exhibit a strong decrease in the number of RFP+ cells in the PCV compared to hhex+/+ (arrowheads point to RFP+ endothelial cells in the PCV). j Quantification of the number of RFP+ endothelial cells across three somites (from two field of view per embryo) in hhex+/? (n = 10) and hhex−/− (n = 4). Values represent means ± s.e.m. ***P ≤ 0.001, and **P ≤ 0.01 by t-test. Scale bars: 50 μm |
|
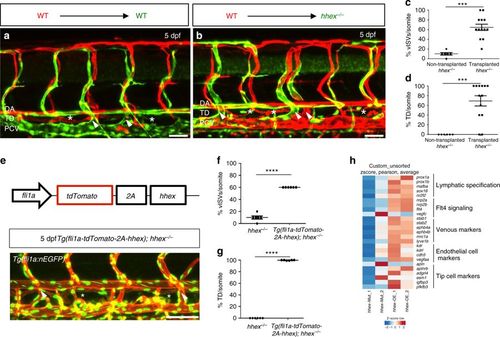
Hhex is required cell-autonomously in endothelial cells to promote venous and lymphatic sprouting in zebrafish. a, b Transplantation of Tg(fli1ep:DsRedEx) donor cells into TgBAC(etv2:EGFP) hosts derived from hhex+/− incrosses. Wild-type endothelial cells contribute to arteries, veins, and lymphatics in wild-type sibling (a) and mutant (b) hosts at 5 dpf (arrowheads point to vISVs; asterisks indicate TD). c, d Quantification of vISVs (c) and TD extensions (d) across four somites in hhex−/− larvae with transplanted wild-type cells (n = 13) vs. hhex−/− larvae without transplanted wild-type cells (n = 6) at 5 dpf. Wild-type endothelial cells can partially rescue both vISV and TD formation in hhex−/−. e hhex endothelial overexpression strategy using the fli1a promoter partially rescues the hhex−/− vascular phenotype (arrowheads point to vISVs; asterisks indicate TD). f, g Quantification of vISVs (f) and TD (g) extensions across four somites in hhex−/− (n = 6) and Tg(fli1a:tdTomato-2A-hhex); hhex−/− (n = 6). h RNA sequencing of 48 hpf FACS-sorted hhex−/− endothelial cells and hhex-overexpressing endothelial cells. Heat map comparisons between these datasets identify Hhex as a regulator of genes implicated in lymphatic specification (prox1a, prox1b, mafba, sox18, nr2f2) and Flt4 signaling (nrp2a, nrp2b, flt4, vegfc) while endothelial cell markers are modulated only by endothelial-specific hhex overexpression. Values represent means ± s.e.m. ****P ≤ 0.0001 and ***P ≤ 0.001 by t-test. Scale bars: 50 μm PHENOTYPE:
|
|
zebrafish hhex mutants exhibit a delay during PHBC formation but form arterial intersegmental vessels (a-b) Maximum intensity projections of confocal images of 24 hpf Tg(fli:nEGFP); hhex+/+ and hhex-/- embryos after GFP immunostaining. hhex mutants exhibit delayed primordial hindbrain channels (PHBCs) formation (arrowheads). (c-d) Maximum intensity projections of confocal images of 48 hpf TgBAC(etv2:EGFP); hhex+/+ and hhex-/- embryos. hhex mutants form arterial ISVs. (e-h) Trunk vasculature of 5 dpf Tg(kdrl:EGFP); Tg(-5.2lyve1b:DsRed); hhex+/+ and hhex-/-. hhex mutants form arterial ISVs while vessels from the PCV (vISVs and TD) are mostly absent (arrowheads point to the ventrally positioned TD; asterisks indicate lack of this structure). i) Quantification of vISVs across 10 somites in 5 dpf hhex+/? (n=8) and hhex-/- (n=8). Values represent means ± s.e.m. ****P ≤0.0001 by t-test. Scale bars: 100 μm (a-b), 200 μm (c-d), 50 μm (e-h). |
|
zebrafish hhex mutants exhibit facial lymphatic defects at 5 dpf (a-b) Facial lymphatic network of 5 dpf Tg(-5.2lyve1b:DsRed); hhex+/+ and hhex-/- larvae; hhex-/- exhibit defects in facial lymphatic vessel formation (arrowheads indicate facial lymphatics, asterisks indicate lack of these structures in hhex mutant). (c-e) Percentage formation of lateral facial lymphatic (LFL) (c), otolithic lymphatic (OLV) (d) and branchial arch lymphatic (LAA) (e) in hhex+/? (n=5) and hhex-/- (n=5). Values represent means ± s.e.m. ****P ≤ 0.0001, **P ≤0.01 and *P ≤ 0.05 by t-test. Scale bars: 100 μm. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
zebrafish hhex is expressed in endothelial cells sprouting from the PCV hhex expression in the zebrafish trunk at 36 (a,b) and 48 (c) hpf by in situ hybridization. hhex is expressed by endothelial cells in the PCV and in vISVs (arrowheads). Transverse section through the embryo indicates expression in the PCV and in the ventral wall of the DA. Scale bars: 50 μm. |
|
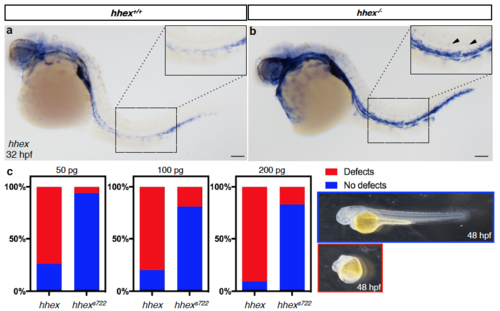
zebrafish hhex mutants exhibit increased hhex expression and the hhexs722 allele appears to encode a non-functional protein (a-b) Whole-mount in situ hybridization showing hhex expression in 32 hpf hhex+/+ and hhex-/- embryos. At 32 hpf, hhex-/- exhibit increased hhex expression in the vasculature (arrowheads point to ISVs). (c) hhex and hhexs722 mRNA injection at 50, 100 and 200 pg into one-cell stage wild-type embryos. Injection of wild-type hhex mRNA, but not hhexs722 mRNA, leads to developmental defects. Scale bars: 100 μm. |
|
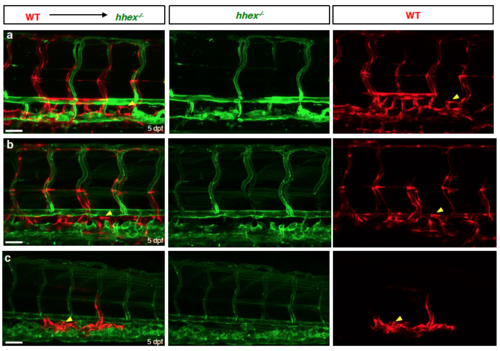
Trunk vascular patterning in 3 different hhex mutants after tranplantation of WT cells. (a-c) Transplantation of wild-type Tg(fli1ep:DsRedEx) donor cells into mutant TgBAC(etv2:EGFP) hosts derived from hhex+/- incrosses. Wild-type endothelial cells contribute to arteries, veins and lymphatics in hhex mutant hosts at 5 dpf (arrowheads point to TD). Scale bars: 50 μm. |
|
Tg(fli1a:tdTomato-2A-hhex) zebrafish embryos develop arteries, veins and lymphatic vessels (a-b) Trunk vasculature of Tg(fli1a:tdTomato-2A-hhex) animals at 3 (a) and 5 (b) dpf. Tg(fli1a:tdTomato-2A-hhex) animals develop arterial, venous and lymphatic vessels (arrows point to vISVs; arrowheads point to parachordal lymphangioblasts (a) or TD (b)). Scale bars: 50 μm. PHENOTYPE:
|

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. |