- Title
-
Identification of Dmrt2a downstream genes during zebrafish early development using a timely controlled approach
- Authors
- Pinto, R.A., Almeida-Santos, J., Lourenço, R., Saúde, L.
- Source
- Full text @ BMC Dev. Biol.
|
Generation and characterisation of the Tg(hsp70:HA-dmrt2a) line. a Transgenic construct design. b Heat-shock protocol: embryos were raised at 28 °C and the heat-shock performed for 30 min at 39 °C. c qPCR analysis showing that dmrt2a transcripts are present from bud-stage until 20-somite stage. d Southern blot hybridisation using a 32P-labelled γ-crystallin probe showing F0 fish with multiple bands (C+, positive control), wildtype fish (C−, negative control), and F1 generation fish with only one copy of the transgene or multiple copies. e The HA-Dmrt2a protein is produced with the correct molecular weight (57 kDa). f The fusion protein HA-Dmrt2a (red) co-localises with the nucleus (blue). h: hours, min: minutes, ss: somite stage. Scale bar: 30 μm EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Characterisation of dmrt2a overexpression phenotype: left-right asymmetry. a Left-sided gene spaw (20-somite stage). b Left-sided gene pitx2 (20-somite stage). c Heart jogging at 30 hpf, using a myl7 probe. d Heart looping at 48 hpf, using a myl7 probe. The embryos shown illustrate the different phenotypes obtained. L: left, R: right, B: bilateral, NAE: no anterior expansion, A: absent, hpf: hours post-fertilisation EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Characterisation of dmrt2a overexpression phenotype: somite clock genes. a deltaC (8-somite stage). b her1 (8-somite stage). c her7 (8-somite stage). The embryos shown illustrate the different phenotypes obtained. Sym: symmetric, S-Asym: slightly asymmetric, Asym: asymmetric EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Characterisation of dmrt2a overexpression phenotype: somite differentiation and formation markers. a Somite differentiation gene pcdh8 (8-somite stage). b Somite boundary gene mespb (8-somite stage). c Muscle differentiation marker myod1 (14-somite stage). d Somite differentiation gene cb1045 (24 hpf). The embryos shown illustrate the different phenotypes obtained. e F-actin staining in control (n = 40/42) and in Tg(hsp70:HA-dmrt2a) after dmrt2a overexpression (n = 22/51) where lack of intersomitic borders is observed (i, ii). Embryos between 8 and 10-somite stage were used. Sym: symmetric, Asym: asymmetric, BD: border defect, hpf: hours post-fertilisation. Scale bar: 45 μm (e) and 20 μm (zoomed panels i and ii) EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. PHENOTYPE:
|

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. |
|
Evaluation of the specificity of dmrt2a-MO. a Alignment between wildtype dmrt2a sequence, dmrt2a Δ100 sequence and dmrt2a-MO. The MO is represented in the sense orientation. In bold caps is represented the start codon, in green the indels and in orange the 3’end of the 5’UTR. b, c Validation of the specificity of dmrt2a-MO using (b) myod1 (14-somite stage) and (c) spaw (20-somite stage). The embryos shown illustrate the different phenotypes obtained in myod1 expression. d, d’ Evaluation of p53 levels by qPCR in (d) Region 1 (somites) and (d’) Region 2 (tailbud/LRO) after injecting dmrt2a-MO in wildtype embryos. UTR: Untranslated Region, L: left, R: right, B: bilateral, NAE: no anterior expansion, Sym: symmetric, Asym: asymmetric, ctrMO: control morpholino, ns: not significant. P-values were generated using a two-tailed t-test EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. |

ZFIN is incorporating published figure images and captions as part of an ongoing project. Figures from some publications have not yet been curated, or are not available for display because of copyright restrictions. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
No misexpression was found in the validated genes after dmrt2a gain and loss-of-function experiments. A1-L2’ In situ hybridisation results depicting the six genes validated in this work. A1-B2” etv2 expression pattern after injecting ctrMO (A1-A1”), dmrt2a-MO (A2-A2”), and after heat-shock in control (B1-B1”) and Tg(hsp70:HA-dmrt2a) (B2-B2”). C1-D2”’ foxj1b expression pattern after injecting ctrMO (C1-C1”’), dmrt2a-MO (C2-C2”’), and after heat-shock in control (D1-D1”’) and Tg(hsp70:HA-dmrt2a) (D2-D2”’). E1-F2” cyp1a expression pattern after injecting ctrMO (E1-E1”), dmrt2a-MO (E2-E2”), and after heat-shock in control (F1-F1”) and Tg(hsp70:HA-dmrt2a) (F2-F2”). G1-H2 cxcl12b expression pattern after injecting ctrMO (G1), dmrt2a-MO (G2), and after heat-shock in control (H1) and Tg(hsp70:HA-dmrt2a) (H2). I1-J2 pxdc1b expression pattern after injecting ctrMO (I1), dmrt2a-MO (I2), and after heat-shock in control (J1) and Tg(hsp70:HA-dmrt2a) (J2). K1-L2’ foxc1b expression pattern after injecting ctrMO (K1, K1’), dmrt2a-MO (K2, K2’), and after heat-shock in control (L1, L1’) and Tg(hsp70:HA-dmrt2a) (L2, L2’). After dmrt2a overexpression using Tg(hsp70:HA-dmrt2a) we did not observe misexpression of the six validated genes. Upon comparison with dmrt2a-MO injected embryos, we observed changes in the expression levels of some genes (arrowheads), according to qPCR data. As depicted with asterisks, after dmrt2a-MO injection we observed only very subtle changes in the expression pattern of some genes, corresponding to the less affected genes, as quantified by qPCR. All embryos were collected between 3 and 4-somite stage (loss-of-function experiments) and between 2 h and 2 h 30 min after heat-shock (gain-of-function experiments). (A1-B2, C1-D2, E1-F2, G1-H2, I1-J2, K1-L2) Lateral view, anterior to the left. (A1’-B2’, C1’-D2’, E1’-F2’) Dorsal-anterior view, anterior to the top. (A1”-B2”, C1”’-D2”’, E1”-F2”, K1’-L2’) Dorsal-posterior view, anterior to the top. (C1”-D2”) Dorsal-medial view, anterior to the top. ctrMO: control morpholino. (TIF 13209 kb) |
|
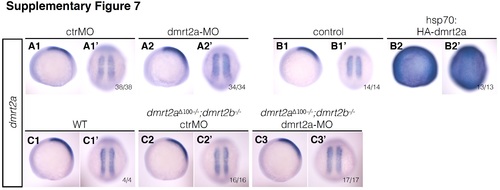
dmrt2a expression pattern using in situ hybridisation after gain and loss-of-function experiments. A1-B2’ dmrt2a expression pattern after injecting ctrMO (A1, A1’), dmrt2a-MO (A2, A2’), and after heat-shock in control (B1, B1’) and Tg(hsp70:HA-dmrt2a) (B2, B2’). C1-C3’ dmrt2a expression pattern in wildtype embryos (C1, C1’), in dmrt2a Δ100−/− ;dmrt2b −/− embryos injected with ctrMO (C2, C2’) and dmrt2a-MO (C3, C3’). (A1-C3) Lateral view, anterior to the left. (A1’-C3’) Dorsal view, anterior to the top. All embryos were collected between 3 and 4-somite stage (loss-of-function experiments) and between 2 h and 2 h 30 min after heat-shock (gain-of-function experiments). ctrMO: control morpholino, WT: wildtype. (TIF 3087 kb) |
|
dmrt2a-MO is specific for the validated genes. A1-F3’ In situ hybridisation results depicting the six genes validated in this work. A1-A3” etv2 expression pattern in wildtype embryos (A1-A1”), in dmrt2a Δ100−/− ;dmrt2b −/− embryos injected with ctrMO (A2-A2”) and dmrt2a-MO (A3-A3”). B1-B3”’ foxj1b expression pattern in wildtype embryos (B1-B1”’), in dmrt2a Δ100−/− ;dmrt2b −/− embryos injected with ctrMO (B2-B2”’) and dmrt2a-MO (B3-B3”’). C1-C3’ cyp1a expression pattern in wildtype embryos (C1, C1’), in dmrt2a Δ100−/− ;dmrt2b −/− embryos injected with ctrMO (C2, C2’) and dmrt2a-MO (C3, C3’). D1-D3 cxcl12b expression pattern in wildtype embryos (D1), in dmrt2a Δ100−/− ;dmrt2b −/− embryos injected with ctrMO (D2) and dmrt2a-MO (D3). E1-E3 pxdc1b expression pattern in wildtype embryos (E1), in dmrt2a Δ100−/− ;dmrt2b −/− embryos injected with ctrMO (E2) and dmrt2a-MO (E3). F1-F3’ foxc1b expression pattern in wildtype embryos (F1, F1’), in dmrt2a Δ100−/− ;dmrt2b −/− embryos injected with ctrMO (F2, F2’) and dmrt2a-MO (F3, F3’). We did not observe obvious differences between the three different conditions evaluated. All embryos were collected between 3 and 4-somite stage. (A1-A3, B1-B3, C1-C3, D1-D3, E1-E3, F1-F3) Lateral view, anterior to the left. (A1’-A3’, B1’-B3’) Dorsal-anterior view, anterior to the top. (A1”-A3”, B1”’-B3”’, C1’-C3’, F1’-F3’) Dorsal-posterior view, anterior to the top. (B1”-B3”) Dorsal-medial view, anterior to the top. ctrMO: control morpholino, WT: wildtype. (TIF 8561 kb) |