- Title
-
Axonemal dynein assembly requires the R2TP complex component Pontin
- Authors
- Li, Y., Zhao, L., Yuan, S., Zhang, J., Sun, Z.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
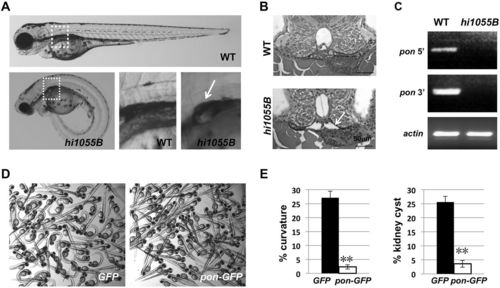
Loss of function of Pontin leads to cilia-associated phenotypes in zebrafish. (A) A wild-type (WT) sibling and a pontinhi1055B/hi1055B (hi1055B) mutant at 3 days post fertilization (dpf). Boxed regions are enlarged in the lower middle and right panels. The mutant shows ventral body curvature and kidney cysts (arrow). (B) Transverse sections of the glomerular neck region of a wild-type sibling and a pontinhi1055B/hi1055B mutant at 50 h post fertilization (hpf). Arrow points to the enlarged lumen in the mutant. (C) Absence of pontin (pon) transcripts in pontinhi1055B/hi1055B mutants. RT-PCR on cDNA from 5 dpf wild-type siblings and pontinhi1055B/hi1055B mutants using primers targeting regions on the 5′ or 3′ side of the proviral insertion. actin is used as a loading control. 40 embryos were pooled per sample. (D) Representative images of embryos at 3 dpf from hi1055B/+ incrosses injected with eGFP or pontin-eGFP mRNA. (E) Significantly reduced frequency of ventral body curvature and kidney cyst in pontin-eGFP mRNA-injected hi1055B/+ incross embryos, as compared with eGFP mRNA-injected control groups. Data are represented as average±s.d. from three independent experiments. **P<0.01. |
|
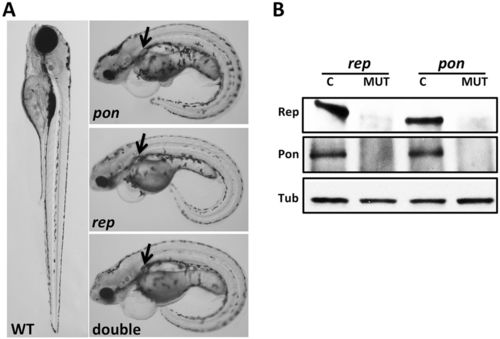
Pontin and Reptin function together in zebrafish development. (A) pontinhi1055B/hi1055B (pon), reptinhi2394/hi2394 (rep) and double mutants at 4 dpf show ventral body curvature and kidney cysts (arrows), as compared with a wild-type embryo. A total of 247 embryos were inspected. (B) Pontin and Reptin depend on each other for protein stability. Total lysates of reptinhi2394/hi2394 (rep, MUT), pontinhi1055B/hi1055B (pon, MUT) and respective control siblings (C) at 4 dpf were subject to IP and blotted with anti-Reptin (Rep) or anti-Pontin (Pon). Western blot of β-Tubulin (Tub) on total lysates was used as a loading control. 20 embryos were used for each sample. The results shown are representative of two independent experiments. |
|
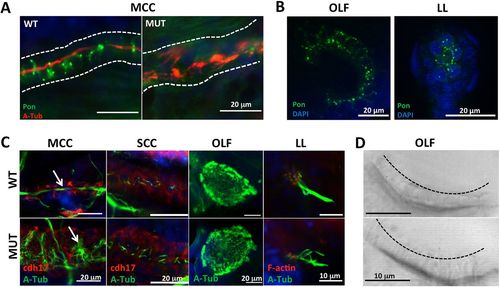
Pontin is a cytoplasmic protein dispensable for cilia morphogenesis. (A) Pontin is enriched in cytoplasmic puncta in the pronephric tubule (outlined) of wild-type zebrafish embryos, but is reduced in pontinhi1055B/hi1055B mutants (MUT) at 2 dpf. Cilia are labeled with anti-acetylated Tubulin (A-Tub; red), Pontin is immunostained in green and nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). MCC, multiciliated cells. (B) Pontin is enriched in cytoplasmic puncta in the olfactory placode (OLF) and the lateral line organ (LL) at 60 hpf. Five embryos were observed. (C) Cilia bundles (arrows) from multiciliated cells in the pronephric tubule, the olfactory placode at 5 dpf and the lateral line organ at 4 dpf in wild type and pontinhi1055B/hi1055B mutants. SCC, single-ciliated cells. Cilia are labeled with anti-acetylated Tubulin (green). Pronephric epithelial cells are labeled with anti-Cdh17 (red). F-actin in hair cells of the lateral line organ is labeled with phalloidin (red). (D) Still images captured from live Nomarski videos showing abundant cilia in the olfactory placode at 3 dpf in both wild type and pontinhi1055B/hi1055B mutants. Dashed line indicates the distal tip of numerous cilia. 10 wild-type and 9 pontinhi1055B/hi1055B mutant embryos were observed. |
|
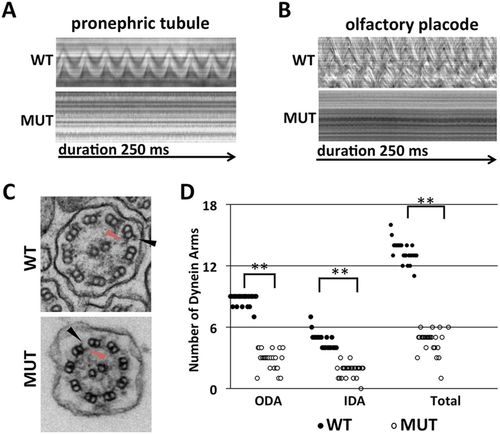
Pontin is essential for cilia motility. (A,B) Kymographs showing the rhythmic beating of motile cilia bundles in the pronephric tubule region (A) and olfactory placode (B) in wild-type zebrafish embryos at 3 dpf. pontinhi1055B/hi1055B mutants (MUT) lack cilia motility. 10 wild-type and 9 pontinhi1055B/hi1055B mutant embryos were observed. (C) Transmission electron micrographs of transverse sections of cilia in the pronephric tubule in wild type and pontinhi1055B/hi1055B mutants at 5 dpf. Black arrowhead, outer dynein arm (ODA); red arrowhead, inner dynein arm (IDA). (D) Reduced number of ODAs, IDAs and total dynein arms per cilium section in pontinhi1055B/hi1055B mutants in comparison with wild-type siblings. n=25. **P<0.01. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
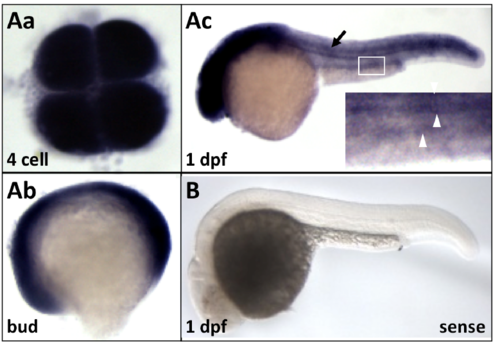
pontin expression during zebrafish development. (Aa-c) In situ hybridization for pontin on wild type embryos fixed at different stages. Black arrow in Ac points to the neural tube. Inset in Ac is an enlarged image of the boxed area. White arrowheads point to the bilateral pronephric tubules. (B) Sense probe control for Ac. |
|
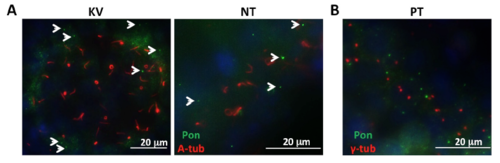
Subcellular localization of Pontin in zebrafish embryos. (A) Pontin distribution in the Kupffer’s vesicle (KV, 8-somite stage) and neural tube (NT, 24 hpf). Cilia are labeled with anti-acetylated-tubulin (A-Tub) in red and Pontin is labeled with anti-Pontin (Pon) in green. White arrowheads point to Pontin puncta. (B) Pontin puncta are not associated with the basal body marker anti-γ-tubulin in the pronephric tubule (PT) at 24 hpf. Pontin is labeled with anti-Pontin (Pon) in green and basal bodies are labeled with anti-γ-tubulin (γ-tub) in red. Nuclei are labeled with DAPI in blue. |