- Title
-
Ectopically expressed Slc34a2a sense-antisense transcripts cause a cerebellar phenotype in zebrafish embryos depending on RNA complementarity and Dicer
- Authors
- Piatek, M.J., Henderson, V., Fearn, A., Chaudhry, B., Werner, A.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS One
|
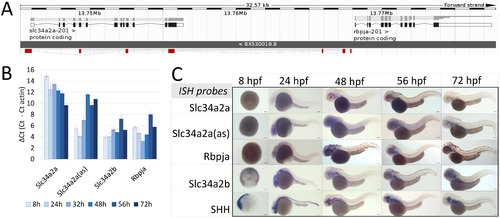
Expression of Slc34a2a and related transcripts during zebrafish embryogenesis. (A) Schematic representation of the Slc34a2a, Slc34a2a(as) and Rbpja loci. The antisense transcript Slc34a2a(as) is depicted in red. (B) RT-qPCR analysis of Slc34a2a, Slc34a2a(as) and Rbpja transcripts including the paralog Slc34a2b. Based on negative controls using RNA as an input, the detection limit was set at a δCt of 12 which is in agreement with ISH results. (C) Demonstration of Slc34a2a, Slc34a2a(as), Rbpja, Slc34a2b and Shh (Sonic Hedgehog) transcripts at progressing stages of development by whole mount ISH. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
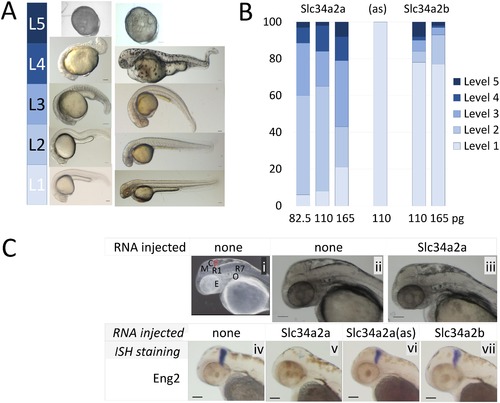
Injection of Slc34a2a RNA into fertilized zebrafish eggs. A) Visual classification of malformations depending on the severity of the defect: Level 1, wild type; level 2, one organ affected (size, shape or function, e.g. heart rate); level 3, 2–3 organs affected, level 4, multiple malformations; level 5, developmental arrest. B) Phenotypic characterization of zebrafish embryos injected with various RNAs, Slc34a2a (554 embryos in total), antisense (94 embryos) and Slc34a2b (538 embryos). C) (i) Anatomy of a 48 hpf zebrafish embryo: Y, yolk sac; E, eye; O, otic vesicle (ear); R1/R7, rhombomeres; M, mesencephalon; C, cerebellum, in red. (ii) non injected wild type embryo; (iii) Slc34a2a injected embryo; (iv) wild type embryo, Eng2 stained; (v) Slc34a2a injected embryo, Eng2 stained; (vi, vii) Slc34a2a(as) and Slc34a2b Eng2 stained. |
|
Injection of Slc34a2a RNA and related constructs into fertilized zebrafish eggs. A) ISH of wild type and injected embryos at 24 hpf. Horizontal labels at the top indicate the injected material, vertical labels, left, represent the probes used for ISH. B) RT-qPCR of injected zebrafish embryos; Slc34a2a, Slc34a2a(as) and Slc34a2b RNA was injected as indicated with the different colour from brown to blue and assayed after 10 and 24 hpf. The left group represents RT-qPCR reactions with Slc34a2a-specific primers; the middle group with Slc34a2a(as)-specific primers and the right group with Slc34a2b-specific primers. The values for non-injected controls are indicated with grey, transparent boxed. |
|
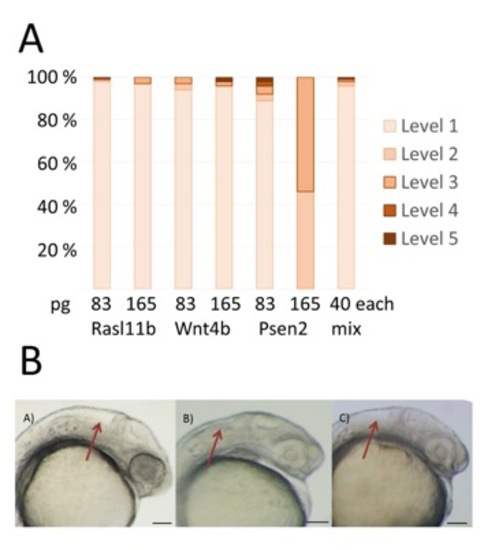
Injection of non- protein coding Slc34a2a RNA and Slc34a2a fragments interfere with zebrafish development. A) Schematic representation of a zebrafish head at 48 hpf; forebrain, blue; eyes, yellow; otic vesicles, green and cerebellum, red. Middle and left, wild type and Slc34a2a-FS injected embryo, respectively. Red arrows indicate the position of the cerebellum. B) Phenotypic quantification of Slc34a2a and Slc34a2a-FS injected embryos (364 Slc34a2a-FS injected embryos were assessed). C) Schematic representation of the fragments generated, even numbers represent sense orientation; uneven numbers, antisense orientation. The large black boxes represent exons comprised in the relevant fragments, the open boxes are exons that are not represented in the injected fragments. The small boxes in red indicate potential sites of hybridization of the injected fragments with an endogenous transcript on the opposite strand. D) Top view of 48 hpf embryos with the fragments (Frag) injected as indicated. E) Phenotypic assessment of injected embryos (90 or more per RNA). F) Eng2 stained embryos injected with the indicated fragments and the relevant controls. All the embryos were tested in parallel with the same solutions and under identical conditions to allow for a comparison of the relative intensities. |
|
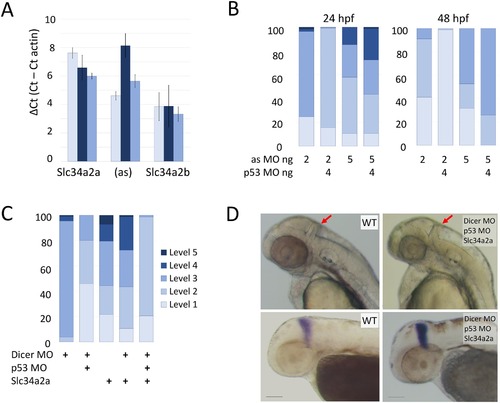
Morpholino knockdown of Slc34a2a(as) and Dicer. A) RT-qPCR quantification of Slc34a2a, Slc34a2a(as) and Slc34a2b after splice site morpholino injection at 24 hpf. Wild type non injected controls, light blue bars; 5 ng splice-site MO injected embryos are in dark blue; 5 ng scrambled MO injected embryos are in blue. B) Phenotypic characterization of MO injected embryos at 24 and 48 hpf. The injected oligonucleotides and quantities are indicated below the bars. Phenotypic scaling was performed as described in Fig 2<. C) Rescue of cerebellum development by Dicer knockdown. Phenotypic assessment of embryos injected with combinations of Dicer MO, p53 MO and Slc34a2a. D) 48 hpf zebrafish embryos injected with Dicer MO, p53 MO and Slc34a2a as indicated in the pictures. In the upper panel, heads with red arrows indicating the cerebellum are shown; the lower panel shows ISH of embryos with an Eng2 probe. |
|
Knockdown of p53 alleviates morpholino toxicity at high concentrations. Non-target specific zebrafish embryo phenotypes can be caused by morpholino toxicity through the activation of p53 mediated apoptosis [59]. Therefore, a p53 morpholino was co-injected with the Dicer UTR morpholino to mitigate toxicity. Co-injection of 4 ng of p53 morpholino caused a partial rescue of 10 ng Dicer UTR injected samples. The rescue was only visible with high concentrations of Dicer UTR morpholino. When 4 ng p53 morpholino were co-injected with 2.5 ng Dicer UTR morpholino, 98.2% of embryos were classified as level 3. The predominant phenotypic feature were shorter body length and non-circular eyes. |