- Title
-
Genetic basis of hindlimb loss in a naturally occurring vertebrate model
- Authors
- Don, E.K., de Jong-Curtain, T.A., Doggett, K., Hall, T.E., Heng, B., Badrock, A.P., Winnick, C., Nicholson, G.A., Guillemin, G.J., Currie, P.D., Hesselson, D., Heath, J.K., Cole, N.J.
- Source
- Full text @ Biol. Open
|
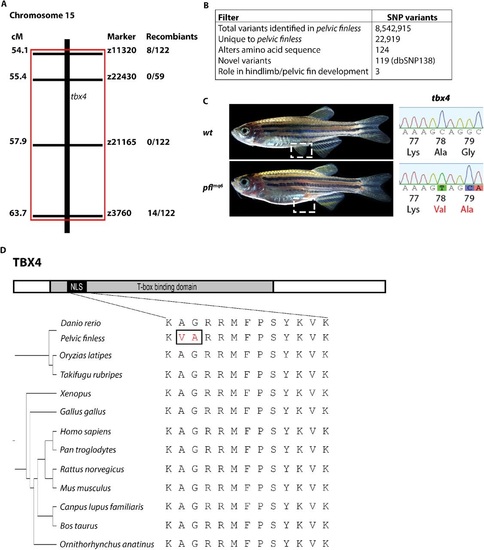
The pelvic finless critical region maps to a region on chromosome 15 containing three SNPs in tbx4. (A) Low and intermediate resolution mapping reveals that the pelvic finless critical region lies between 54.1 and 63.7cM on chromosome 15. (B) Region-specific, targeted-enrichment next generation sequencing filtering process revealed three SNPs in tbx4. (C) The three SNPs in exon 3 of tbx4 of pelvic finless zebrafish are predicted to cause two amino acid substitutions (A78V and G79A). (D) Schematic diagram of the conservation of vertebrate TBX4 nuclear localization signal (NLS). The NLS is located within the highly conserved T-box domain of the protein. The sequence of the TBX4 NLS is perfectly conserved amongst vertebrates with hindlimbs or pelvic fins, pelvic finless zebrafish exhibit variations in this motif. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Mutations in the Tbx4 NLS sequence cause the loss of pelvic fins in pelvic finless zebrafish. (A) Wild-type zebrafish (tbx4+/+) pelvic fins are located on the posterior ventral flank of the fish, either side of the cloaca. (B) TALENs-induced mutated tbx4 causes the loss of pelvic fins in homozygous tbx4 mutation zebrafish (tbx4gi1/gi1). (C) Heterozygous mutant tbx4 zebrafish (tbx4gi1/+) display normal pelvic fin development. (D) Pelvic finless zebrafish (pflmq6/mq6) do not develop pelvic fins due to missense mutations in the Tbx4 NLS. (E) Pelvic finless; mutant tbx4 compound heterozygotes (tbx4gi1/mq6) also do not develop pelvic fins. (F) Heterozygous wild-type; pelvic finless zebrafish (pflmq6/+) develop pelvic fins, confirming that the pelvic finless mutation is allelic to tbx4 and that the mutations in the NLS of Tbx4 (A78V; G79A) result in a loss of function of the tbx4 gene. White rectangle in A-F indicates zoomed in region shown in A′-F′. Scale bars: 1mm. |
|
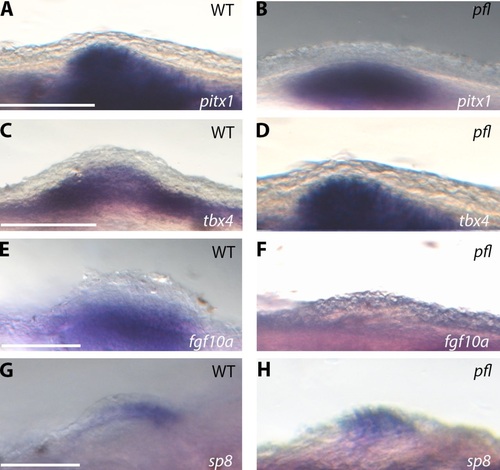
Mutations in the Tbx4 NLS cause altered expression of pelvic fin outgrowth genes. (A,B) pelvic finless zebrafish express the hindlimb initiation gene pitx1 in the developing pelvic fin mesenchyme in a similar pattern to wild-type zebrafish. (C,D) pelvic finless zebrafish express tbx4 mRNA in the developing pelvic fin mesenchyme in a similar pattern to wild-type zebrafish. (E,F) There is no detected expression of fgf10a mRNA in the developing pelvic fin regions of pelvic finless zebrafish, whilst fgf10a expression is observed in the developing pelvic fin mesenchyme of wild-type zebrafish. (G,H) Altered expression of the apical ectodermal ridge marker, sp8, is observed in pelvic finless zebrafish. In pelvic finless zebrafish the expression of sp8 mRNA is not restricted to the apical ectodermal thickening, as seen in wild-types, but is diffuse in the apical ectodermal thickening precursor cells which have failed to accumulate in the dorsoventral boundary in pelvic finless zebrafish (n=24). Scale bars: 50µm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|