- Title
-
rbm 47, a novel RNA binding protein, regulates zebrafish head development
- Authors
- Guan, R., Ei-Rass, S., Spillane, D., Lam, S., Wang, Y., Wu, J., Chen, Z., Wang, A., Jia, Z., Keating, A., Hu, J., and Wen, X.Y.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Dyn.
|
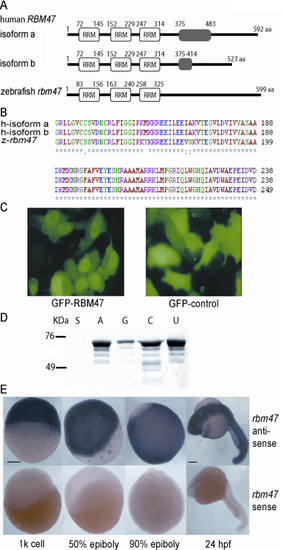
Characterization of human and zebrafish RBM47. A: Diagrammatic representation of human and zebrafish RBM47 (Rbm47) proteins (not to scale). Human RBM47 gene encodes two alternatively spliced transcripts, resulting in two protein isoforms a and b. The gray box indicates the nonhomology region resulting from alternative splicing. Zebrafish rbm47 gene encodes only one isoform. All proteins possess three RRM domains. B: Sequence alignment of highly conserved regions of human and zebrafish RBM47 (Rbm47) RRMs. The zebrafish Rbm47 RRM has 90% sequence identity compared with those of the human orthologue. C: HeLa cells transfected with RBM47-GFP fusion plasmid express RBM47 in the nucleus, compared with control-transfected cells that express green fluorescent protein (GFP) throughout the cell. D: The RNA binding assay demonstrates RBM47′s ability to bind poly-A, -U, and -C RNA, while weakly binding poly-G RNA, and having no affinity for single-stranded DNA as shown in lane S. E: rbm47 is expressed ubiquitously during zebrafish embryogenesis, as shown by whole mount in situ hybridization. Scale bar = 200 µm. |
|
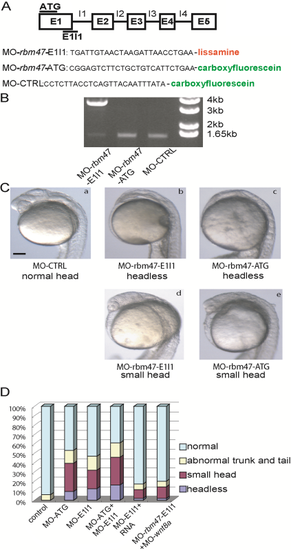
rbm47 knockdown in developing zebrafish embryos disrupts head formation. A: Two morpholino knockdown strategies were used to disrupt rbm47 function. MO-rbm47-ATG hybridizes to the start codon, preventing translation initiation. MO-rbm47-E1I1 hybridizes to the exon-1/intron-1 splice donor site, blocking splicing to exon 2. Schematic drawing is not to scale. B: Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was used to show interrupted splicing of RNA extracted from MO-rbm47-E1I1 zebrafish, which amplifies a band of approximately 3.5 kb due to retention of intron 1. PCR cycles: lane 1 (34 cycles); lane 2 (30 cycles); lane 3 (30 cycles). C: Upper panels demonstrate typical loss of head phenotype in rbm47 knockdown zebrafish (b and c) and a control zebrafish injected with control morpholino (a). The lower panels depict typical small head phenotypes in MO-rbm47 injected fish (d and e). Scale bar = 200 µm. D: The incidence of total loss of head development in morpholino-injected zebrafish. Injection of morpholinos targeting rbm47 resulted in a 9-16% incidence of the headless phenotype. Co-injection of rbm47 mRNA or wnt8a blocking morpholino with rbm47 blocking morpholino resulted in a decreased incidence of headlessness (for detailed numbers and statistics, see Table 1). PHENOTYPE:
|
|
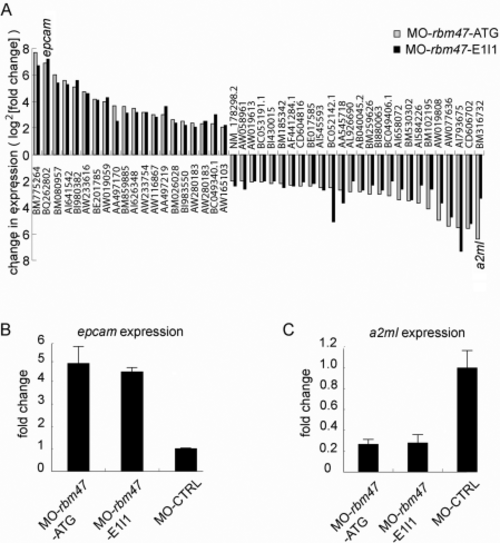
RNA microarray to identify candidate rbm47 target genes. A: Twenty genes were found to be up-regulated and 26 genes were found to be down-regulated by at least four-fold as shown on the left and right side of the graph, respectively. B,C: Confirmation of the most significantly up- and down-regulated genes by real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (epcam and a2ml). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|