- Title
-
Differential Role of Axin RGS Domain Function in Wnt Signaling during Anteroposterior Patterning and Maternal Axis Formation
- Authors
- Schneider, P.N., Slusarski, D.C., and Houston, D.W.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS One
|
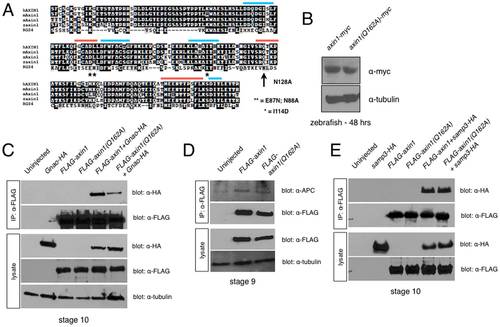
Structure-function analysis of the Axin1 RGS domain. (A) Alignment of RGS domains from human (hAXIN1), mouse (mAxin1), Xenopus (xAxin1) and zebrafish Axin1 (zAxin1) with human RGS4. Blue bars = APC binding interface; orange bars = Gna binding interface. * = residues required for GAP activity in RGS4. Arrow = residue required for RGS4 GAP activity, mutated in this study. (B) Immunoblots showing equivalent protein expression in 24 hpf zebrafish embryos injected with axin1-myc and axin1(Q162A)-myc. (C) Immunoprecipitation of FLAG-tagged Axin1 constructs with HA-tagged Gnao, showing reduced binding of FLAG-Axin1(Q162A) to overexpressed Gnao. (D) FLAG-Axin1 and FLAG-Axin1(Q162A) immunoprecipitate endogenous APC equivalently. (E) FLAG-Axin1 and FLAG-Axin1(Q162A) immunoprecipitate HA-tagged APC-SAMP3 equivalently. |
|
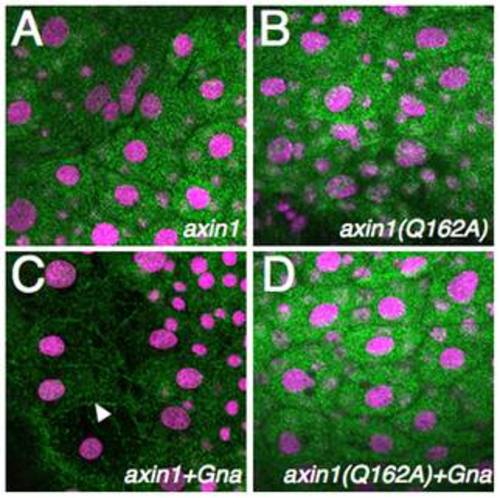
Axin1Q162A does not interact with Gna at the plasma membrane. (A–D) Immunostaining against Myc showing localization of Axin1-Myc and Axin1(Q162A)-myc in zebrafish embryos, without (A, B) or with coexpression of Gnao (C, D). The arrowhead in C indicates membrane localization of Axin1 upon Gnao expression. Embryos were counterstained with TOPRO3 to show nuclei (purple). |
|
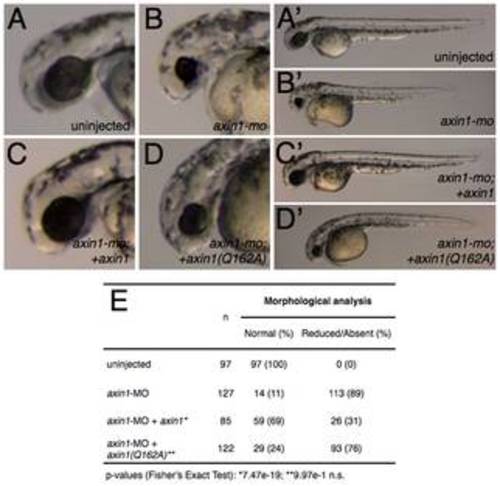
axin1 but not axin1(Q162A) rescues anterior defects in Axin1-depleted embryos. (A–D′) Representative phenotypes of control and Axin1-depleted zebrafish embryos. (A) control uninjected embryo, (B) Axin1-depleted embryo (4 ng axin1-MO), (C) MO injected embryo coinjected with 25 pg axin1 mRNA, (D) MO injected embryo coinjected with 25 pg axin1(Q162A) mRNA. (E) Summary table of morphological defects. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
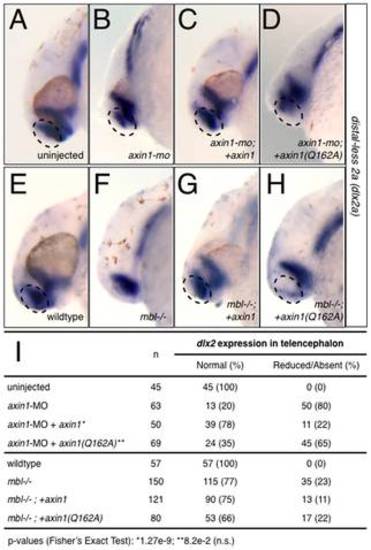
axin1 but not axin1(Q162A) rescues telencephalic defects in Axin1-depleted and in mbl-/- embryos. (A–H) Representative examples of dlx2 expression in control and Axin1-depleted zebrafish embryos (A–D) and in wildtype and mbl-/- embryos (E–H). (A) control uninjected embryo at 24 hpf, (B) axin1-MO-injected, (C) axin1-MO+xx axin1, (D) axin1-MO+axin1(Q162A), (E) wildtype embryo at 24 hpf, (F) mbl-/-, (G) mbl-/-;+axin1 (H) mbl-/-;+axin1(Q162A). (I) Summary of dlx2 expression data. Arrows indicate areas of reduced or absent dlx2 in the telencephalon. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|