- Title
-
Maternal topoisomerase II alpha, not topoisomerase II beta, enables embryonic development of zebrafish top2a-/- mutants
- Authors
- Sapetto-Rebow, B., McLoughlin, S.C., O'Shea, L.C., O'Leary, O., Willer, J.R., Alvarez, Y., Collery, R., O'Sullivan, J., Van Eeden, F., Hensey, C., and Kennedy, B.N.
- Source
- Full text @ BMC Dev. Biol.
|
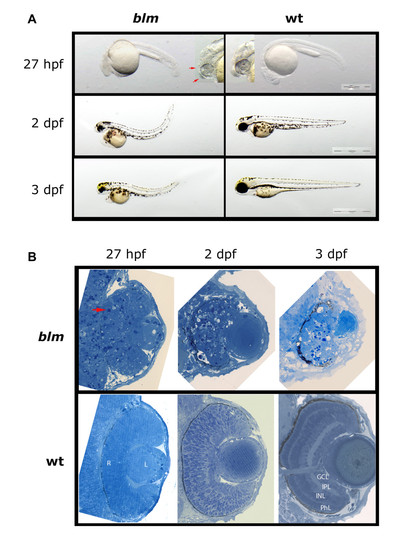
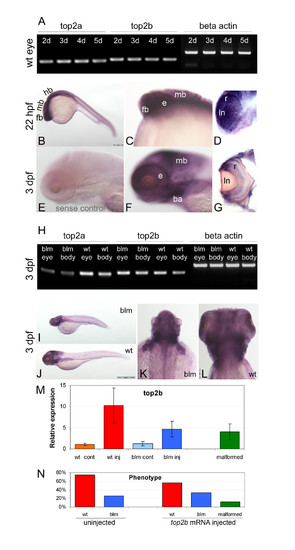
Phenotype of the zebrafish bloody minded (blm) mutant. A) Mutants can be first recognized at ~27 hpf when signs of malformation in the head are visible (red arrows). At 2 and 3 dpf, eyes are much smaller and the tail is bent dorsally. B) Plastic sections through the eye reveal apoptotic cells in the retina (red arrow) and in the brain at 27 hpf. There is no proper lamination of the retina and necrosis proceeds. Abbreviations: hpf - hours post fertilisation, dpf - days post fertilisation, R - retina, L - lens, PhL - photoreceptor layer, INL - inner nuclear layer, IPL - inner plexiform layer, GCL - ganglion cells layer. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
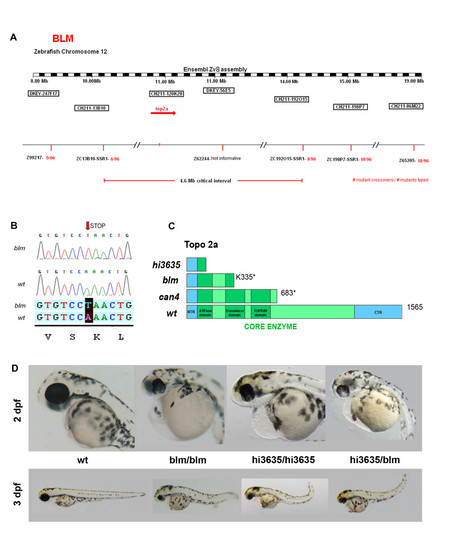
blm arises from a mutation in the top2a gene. A) Mapping of blm reveals that the gene is located on chromosome 12. B) top2a was selected as a candidate gene and sequencing of mutant cDNA shows a point mutation (A→T) in Lys residue 335 resulting in a premature stop codon. C) A schematic of wildtype Top2a protein and the truncated proteins in hi3635, blm and can4 mutants D) Complementation assay performed to confirm that blm is top2a mutation. blm heterozygotes were crossed to hi3635 carriers and the resulting hybrid offspring present with blm phenotype. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
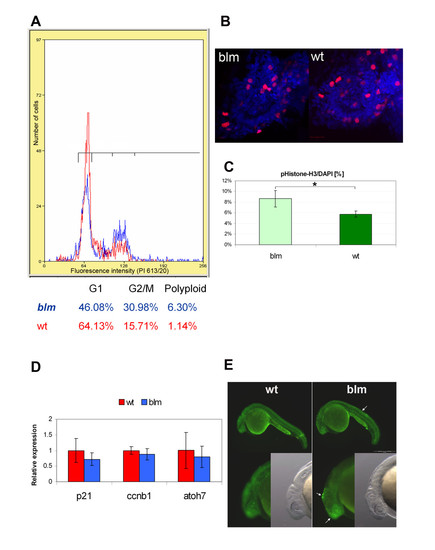
top2a mutants exhibit defects in cell cycle progression. A) Flow cytometry analysis of larvae at 27 hpf (red plot - wt, blue - blm) reveals an increased fraction of cells in G2/M phase in blm mutants. B) Representative Z-series projections showing that the total number of mitotic cells (stained with PH3 antibody - red) is lower in the eye of 27 hpf blm mutants (n = 58) than in wild type larvae (n = 70). C) The percentage of mitotic cells (PH3 positive) relative to the total number of DAPI stained cell nuclei is significantly (p = 0.036) higher in blm mutants compared to wild type as assessed from n e 23 sections through the head and spinal cord of the N = 5 mutant and wild type larvae. D) Real time PCR of cell cycle markers p21-like (G1 phase) and ccnb1 (G2/M phase) in wildtype and blm larvae at 27 hpf shows no significant difference in expression levels (p = 0.21 and 0.38, respectively). Expression of atoh7, a marker of retinogenesis, is also equivalent in eyes of blm and wildtype siblings. Presented data are average of 3 replicate experiments, each comprising pools of 16-35 larvae. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean (C-D). E) Acridine orange staining of apoptotic cells in wildtype and blm larvae at 24 hpf. Arrows point to regions of increased apoptosis in blm mutants. |
|
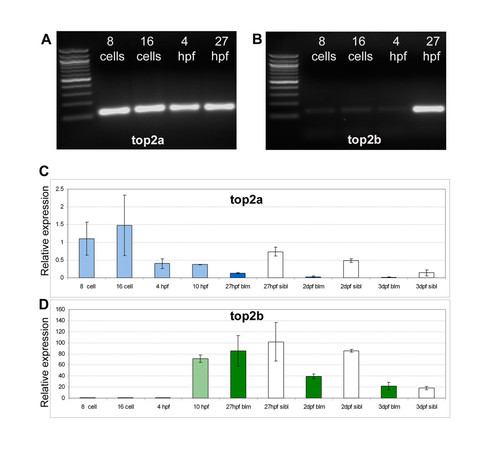
top2a, but not top2b, is expressed pre-MZT. RT-PCR of wt embryos (A-B) and real time PCR of offspring from blm carriers (C-D) shows that maternal top2a (A, C), but not top2b (B, D), is present pre-MZT at 8- and 16-cell stages. top2a transcript levels decrease in blm siblings from 27 hpf to 3 dpf, and the expression in blm mutants is always significantly lower (C). The levels of top2b transcript also decrease in wildtype siblings from 27 hpf to 3 dpf, and although top2b levels in blm mutants and siblings is similar at 27 hpf, top2b is dramatically reduced in the mutants by 2 dpf (D). Error bars represent the standard error of the mean. At 8-cell, 16-cell, 4 hpf and 10 hpf stages mutant and wild type offspring are pooled. In graphs light blue (C) and light green bars (D) represent pooled wiltype and mutant embryos; dark blue/green bars represent blm mutants and white bars represent wildtype larvae. |
|
Overlapping expression, but functional divergence of top2a and top2b paralogues in vivo. A) RT-PCR shows that both top2a and top2b are expressed in the eye at 2, 3, 4 and 5 dpf. B-G) Wholemount in situ hybridization reveals that top2b is expressed in the anterior of wildtype larvae including the forebrain, midbrain and eye (B-D) at 22 hpf and in the forebrain, midbrain, branchial arches and retina (F-G) at 3 dpf. E is the negative control sense probe; D and G are sections through the eye. H) RT-PCR at 3 dpf shows similar abundant expression of top2b in the eye and body of blm mutants and wildtype sibling. I-L) Wholemount in situ hybridization reveals a similar spatial expression pattern of top2b in blm (I, K) and wildtype larvae (J, L) at 3 dpf. M) top2b expression levels at 33 hpf following injection of top2b mRNA into 1-2 cell stage offspring of blm carriers. blm larvae overexpressing top2b RNA by 2.7-5.9 fold show no evidence of phenotypic rescue. N = 3 replicate experiments, n = 50 uninjected wild type (wt cont), n = 29 top2b RNA injected wild type (wt inj), n = 13 uninjected blm (blm cont), n = 17 top2b RNA injected blm (blm inj), n = 6 top2b RNA injected malformed. N) Phenotypes recorded at 33 hpf following injecting offspring of carriers of blm mutation with zebrafish top2b mRNA (N e 3 replicate experiments, n = 117 uninjected wild type, n = 40 uninjected blm, n = 29 top2b RNA injected wild type, n = 17 top2b RNA injected blm, n = 6 top2b RNA injected malformed). Error bars represent the standard error of the mean. Abbreviations: ba - branchial arches, e - eye, fb - forebrain, hb - hindbrain, ln - lense, mb - midbrain, r - retina. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
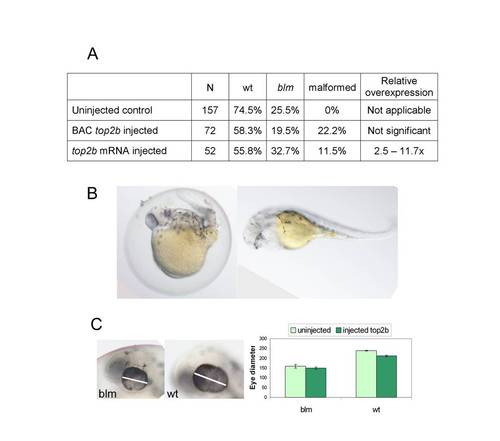
Overexpression of top2b in blm embryos. Offspring of blm carriers were microinjected at 1-2 cell stages with zebrafish genomic top2b sequence (BAC clone CHORB736O22185Q) at 25 ng/μl (7.5 pg per embryo) or zebrafish top2b mRNA at 250 ng/μl (75 pg per embryo) and analysed at 33 hpf. A) Table of observed phenotypes upon injecting offspring of carriers of blm mutation with zebrafish top2b BAC clone or in vitro synthesised top2b RNA. B) Images of 33 hpf malformed larvae overexpressing top2b by ~4 fold following injecting with top2b mRNA. C) Ectopic expression of top2b mRNA does not rescue the small eye phenotype of blm embryos. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean. |
|
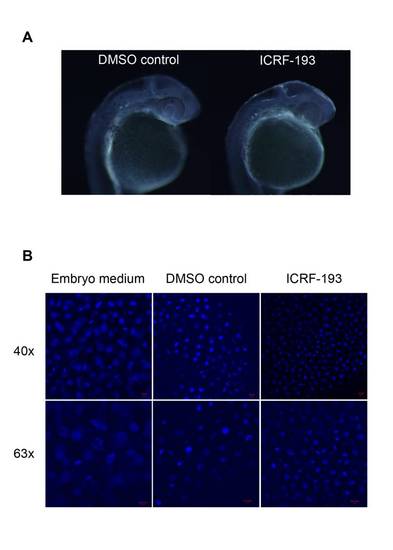
Transient inhibition of Top2a pre-MZT. A) Dark field images showing the morphology of embryos at 27 hpf following treatment with ICRF-193 from 1-2 cell stage until 3.5 hpf B) Representative confocal images (projections of 30 slices taken at 0.5 μm intervals) of 3.5 hpf embryos stained with DAPI, which had been treated from 1-2 cell stage with 100 μM ICRF-193. Chromatin appears to be more compacted in the treated embryos but not extensive DNA damage was observed. |
|
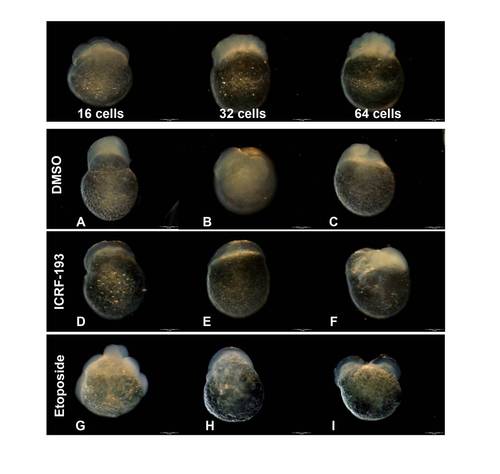
Staging of embryos treated with topoisomerase inhibitors. Top panel: images of normally developed embryos at 16, 32 and 64 cell stages. Bottom panels: example images of "not classified" or malformed embryos treated with 1% DMSO (vehicle control), ICRF-193 or etoposide. This group includes embryos with atypical shape: A) irregular shape, protruding animal pole, B) asymmetric animal pole and uneven cell size, C) irregular shape and opaque, D-E) undefined cell morphology and abnormal transparency, F) small, irregular-shaped animal pole, G) abnormal distribution of cells around yolk, H) undefined cell morphology with abnormal distribution around yolk, I) duplicated/split animal pole. |

Unillustrated author statements |