- Title
-
Pbx1 is essential for growth of zebrafish swim bladder
- Authors
- Teoh, P.H., Shu-Chien, A.C., and Chan, W.K.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Dyn.
|
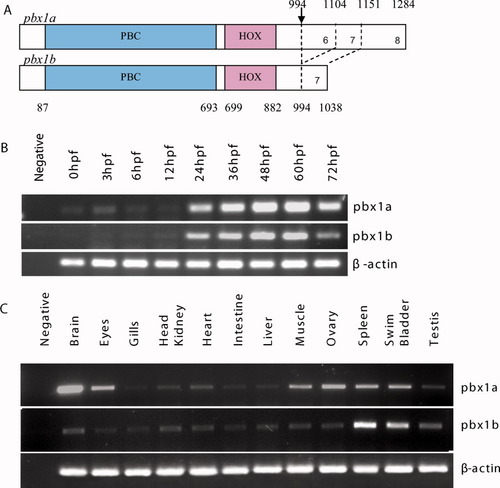
Pbx1 protein structure and reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) expression pattern analysis. A: Protein domains of zebrafish Pbx1a and Pbx1b. Numbers refer to amino acid residues. The location of the alternatively spliced exon is marked by an arrow. Exons 1 to 5 are common to both Pbx1 isoforms. B: RT-PCR temporal expression pattern of zebrafish pbx1a and pbx1b during early embryonic development. Sizes of the amplified products were 641 bp for pbx1a, 530 bp for pbx1b, and 200 bp for β-actin. C: Expression of pbx1a and pbx1b in adult tissues obtained from 6-month-old zebrafish. |
|
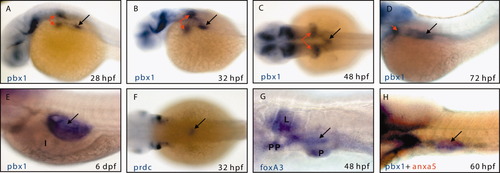
Expression of pbx1 in the head region. A-D: Lateral view at 24 (A), 36 (B), 60 (C), and 72 hpf (D). E-H: Dorsal view at 24 (E), 36 (F), 60 (G), and 72 hpf (H) of pbx1 expression in the forebrain (FB), midbrain (MB), and hindbrain (HB). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Spatio-temporal expression of pbx1 at the trunk region. A-D: Posterior pharyngeal arches (5th-7th arches) seen as early as 28 hpf located bilaterally anterior to the first somite. A: Expression of pbx1 in the swim bladder anlage at 28 hpf. B: Swim bladder anlage at 32 hpf. C: Swim bladder bud at 48 hpf. D: Elongated swim bladder sac at 72 hpf. E: Inflated swim bladder at 6 dpf. F: prdc expression in the swim bladder overlapped with pbx1 at 32 hpf. G: foxA3 expression at the swim bladder bud and other gut-derived organs at 48 hpf. H: Colocalization of pbx1 (blue) and anxa5 (red) in the swim bladder at 60 hpf. I, intestine; L, liver; PP, posterior pharynx; P, pancreas; black arrow, swim bladder; red arrow, posterior pharyngeal arches. |
|
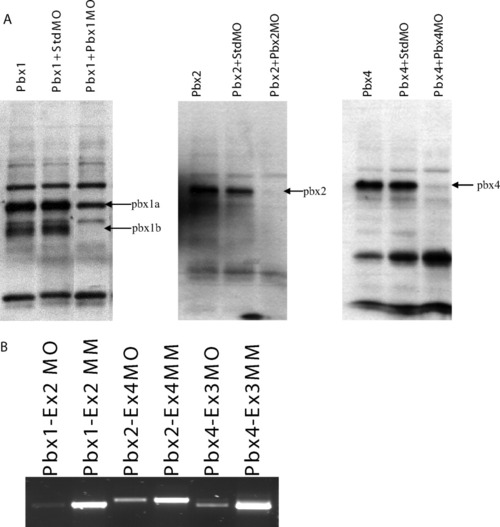
Efficacy of pbx morpholinos. A: Efficiency of translation-blocking morpholinos (Pbx1MO, Pbx2MO, Pbx4MO) in blocking translation as shown by in vitro translation of corresponding mRNA alone, with standard control antisense morpholino (StdMO) or with morpholinos. B: Efficacy of splice-blocking morpholinos. RT-PCR shows decreased mRNA expressions level for embryos injected with splice-blocking morpholino (Pbx1-Ex2MO, Pbx2-Ex4MO, Pbx4-Ex3MO) as compared to their respective missense control (Pbx1-Ex2MM, Pbx2-Ex4MM, Pbx4-Ex3MM). |
|
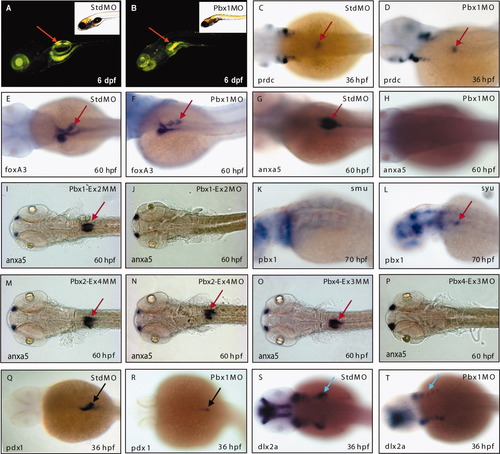
Morpholino-mediated knockdown of pbx1 disrupts swim bladder, pancreas, and pharyngeal arches development. A,B: Swim bladder development in 6-dpf gut GFP transgenic embryo injected with StdMO (A) and Pbx1MO (B) showing non-inflated swim bladder in pbx1 morphants. C-H: In situ hybridization of swim bladder markers prdc, foxA3, and anxa5 using embryos injected with StdMO and Pbx1MO at 36 (C, D), 48 (E,F), and 60 hpf (G,H). I,J: In situ hybridization for anxa5 in 60-hpf embryos injected with Pbx1-Ex2MM (I) and Pbx1-Ex2MO (J). K,L: Expression of pbx1 in mutants deficient in hedgehog signaling. Reduced pbx1 expression in the syu mutant at 72 hpf (K) and absence of expression of pbx1 in the swim bladder of smu mutant at 72 hpf (L). M-P: Splice-blocking morpholino-mediated knockdown of pbx2 or pbx4 disrupts swim bladder development. In situ hybridization for anxa5 in 60-hpf embryos injected with Pbx2-Ex4MM (M) and Pbx2-Ex4MO (N), Pbx4-Ex3MM (O), and Pbx4-Ex3MO (P). Q,R: In situ hybridization for pancreas marker, pdx-1, in 36-hpf embryos injected with StdMO (Q) and Pbx1MO (R). S,T: In situ hybridization for dlx2a, a pharyngeal arches marker in 36-hpf embryos injected with StdMO (S) and Pbx1MO (T). Red arrow, swim bladder; black arrow, pancreas; blue arrow, posterior pharyngeal arches. |