- Title
-
Maternal and zygotic aldh1a2 activity is required for pancreas development in zebrafish
- Authors
- Alexa, K., Choe, S.K., Hirsch, N., Etheridge, L., Laver, E., and Sagerström, C.G.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS One
|
88.21 is a novel aldh1a2 allele. A, B. Islet1 (isl1) expression was used in a haploid ENU screen to identify mutants in endocrine pancreas development. Dorsal view of 30 hpf wild type embryo with isl1 expression in the CNS and endocrine pancreas (A; black arrow indicates expression in pancreas) and 88.21 mutant embryo with isl1 expression in the CNS, but not in the endoderm (B). C–E. Lateral view of live wild type (C), 88.21 (D), and neckless aldh1a2i26 (E) embryos at day 5. F. Linkage analysis using CA repeat markers on pooled genomic DNA from 88.21 mutants and pooled genomic wild type DNA. Marker z10441 amplifies a 450 bp band and a faint 500 bp band in the mutant pool compared to a faint 450 bp band and a 500 bp band in the wild type pool. Marker z8693 amplifies two bands at 250 bp and 300 bp in the mutant pool compared to 250 bp, 300 bp as well as a 400 bp band in the wild type pool. White arrow points to lack of 400 bp band in mutant. G. Schematic drawing of part of linkage group 7 (LG7), showing the location of z10441 and z8693 and aldh1a2 (in red) in reference to these markers. H–J. Sequence analysis of pooled 88.21 mutant (MT) genomic DNA and pooled wild type (WT) genomic DNA (H, J), as well as of individual mutant (MT) and wild type (WT) embryos (I). 88.21 fish carry a mutation that converts Gly484 to Arg (in red, and outlined in brackets in J) located in the catalytic domain. K. Schematic of Aldh1a2 protein and the location of the aldh1a2 mutant alleles aldh1a2i26, aldh1a2u11 and 88.21/aldh1a2um22. |
|
Wild type aldh1a2 mRNA rescues 88.21 fin bud development. Dorsal views of 48 hpf embryos with sonic hedgehog (shh) expression in purple. A. Uninjected wild type embryo with shh expression in the CNS and fin buds (black arrows). B. aldh1a2um22 mutant embryos lack shh expression in the fin buds. C. aldh1a2um22 mutant embryo injected with aldh1a2 wild type mRNA shows rescued fin bud expression (black arrows). D. aldh1a2um22 mutant embryo injected with aldh1a2um22 mutant mRNA is not rescued. |
|
aldh1a2um22 and aldh1a2i26 mutant embryos retain some endoderm gene expression at 24 and 30 hpf. DMSO treated wild type embryos (A, E, I, M), DEAB-treated wild type embryos (B, F, J, N), embryos from an incross of aldh1a2um22 heterozygotes (C, G, K, O) and embryos from an incross of aldh1a2i26 heterozygotes (D, H, L, P) were assayed for expression of ins at 24 hpf (A–D; black arrows indicate residual expression), pdx1 at 24 hpf (E–H; black arrows indicate residual expression), hhex at 30 hpf (I–L; residual expression is indicated in pancreas (arrow) and liver (arrowhead)) and prox1 at 30 hpf (M–P; residual expression is indicated in liver (arrowhead)). Embryos are in dorsal view with anterior to the left. See Table 2 for quantification. |
|
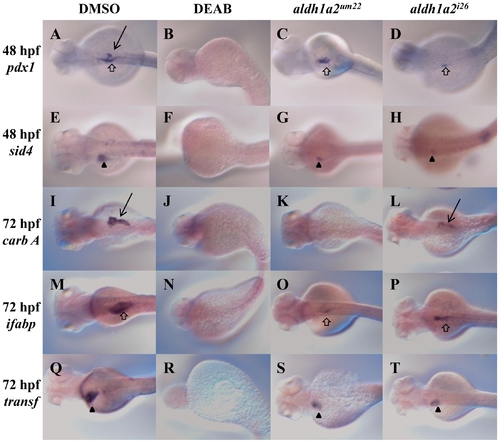
aldh1a2um22 and aldh1a2i26 mutant embryos retain some endoderm gene expression at 48 and 72 hpf. DMSO treated wild type embryos (A, E, I, M, Q), DEAB-treated wild type embryos (B, F, J, N, R), embryos from an incross of aldh1a2um22 heterozygotes (C, G, K, O, S) and embryos from an incross of aldh1a2i26 heterozygotes (D, H, L, P, T) were assayed for expression of pdx1 at 48 hpf (A–D), sid4 at 48 hpf (E–H), carbA at 72 hpf (I–L), ifabp at 72 hpf (M–P) and transf at 72 hpf (Q–T). Gene expression is observed in the intestine (open arrows), liver (black arrowheads) and pancreas (black arrows). Embryos are in dorsal view with anterior to the left. See Table 2 for quantification. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
aldh1a2 is maternally expressed and aldh1a2 translational morpholino knocks down endoderm expression. A. PCR of 3 and 6 hpf wild type embryos using primers targeting exon1-2 and exon10-11 of aldh1a2 reveals aldh1a2 expression already at 3 hpf. A no DNA sample and amplification of tubulin is used as negative and positive controls. B–G. Wild type embryos were injected with either 950 uM aldh1a2 mismatch (mm) morpholino (MO; B, D, F) or 950 uM of aldh1a2 translational (tMO; C, E, G) and assayed for expression of hhex (B, C), prox1 (D, E) or pdx1 (F, G). Embryos are in dorsal view with anterior to the left. |
|
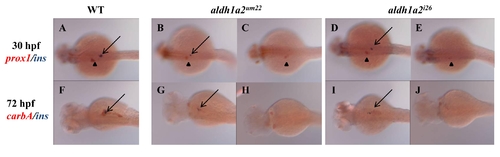
Double in situ in aldh1a2um22 and aldh1a2i26 mutant embryos. Wild type (A, F), aldh1a2um22 (B, C, G, H) and aldh1a2i26 (D, E, I, J) embryos were assayed for expression of prox1/ins at 30 hpf (A-E) and carbA/ins at 72 hpf (F-J). Ins expression is detected in purple, while prox1 (A-E) and carbA (F-J) are detected in red. We do not observe any correlation in the extent of residual expression by these genes in individual embryos. |
|
Titration of DEAB and aldh1a tMO. Wild type (A), aldh1a2um22 mutant (B), aldh1a2i26 mutant (C), DEAB-treated (D-G) and aldh1a2 tMO-injected (H-K) embryos were assayed for pdx1 expression at 48 hpf. DEAB and aldh1a2 tMO was titrated as indicated (D-G and H-K, respectively). Black arrows indicate pancreas expression and open arrows indicate duodenum expression of pdx1. Note that intermediate concentrations of DEAB (1 μM, panel E) and aldh1a2 tMO (250–500 uM, panels I, J) produce similar phenotypes to the aldh1a2um22 and aldh1a2i26 mutants. Embryos are in dorsal view with anterior to the left. |

Unillustrated author statements EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|