- Title
-
Expression screening and annotation of a zebrafish myoblast cDNA library
- Authors
- Baxendale, S., Chen, C.K., Tang, H., Davison, C., Hateren, L.V., Croning, M.D., Humphray, S.J., Hubbard, S.J., and Ingham, P.W.
- Source
- Full text @ Gene Expr. Patterns
|
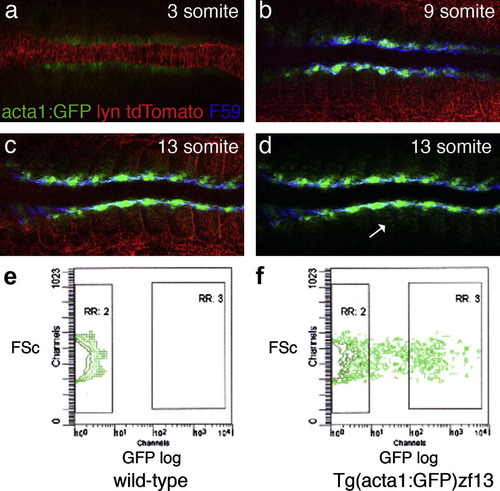
GFP expression and FACS analysis of Tg(acta1:GFP)zf13 embryos. (a–d) Dorsal view of flat-mounted Tg(acta1:GFP)zf13 embryos at 3, 9 and 13 somite stages, anterior to the left. Embryos were injected with Lyn:tdTomato RNA to highlight the cell membranes (red) and immunohistochemistry with F59, specific for slow myosin heavy chain (Devoto et al., 1996), labeled the slow myoblast cells blue. (a) Three somite stage embryo. GFP is weakly expressed in the adaxial cells flanking the notochord. No F59 stain can be detected at this stage. (b) Nine somite stage embryo. GFP is seen in adaxial cells, which are co-stained with F59. (c) Thirteen somite stage embryo. The strongest GFP expression is medial next to the notochord. The most anterior adaxial cells are elongated and have slow twitch myofibrils detected by F59. Weaker GFP expression is seen in the fast twitch fibre precursors. (d) The same picture as (c) with the red channel omitted. The weaker GFP-expressing cells are seen clearly in the posterior half of the somite; the site of early myoD expression where the first fast myoblast cells differentiate. (e and f) FACS analysis of dissociated Tg(acta1:GFP)zf13 embryos. Each plot shows the forward scatter (FSc) plot of the single cell population (x-axis) against GFP fluorescence (y-axis). In wild-type embryos (1E) no fluorescence is detected. In GFP-expressing embryos cells show a range of fluorescence with 12.5% of cells expressing GFP strongly (RR:3). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
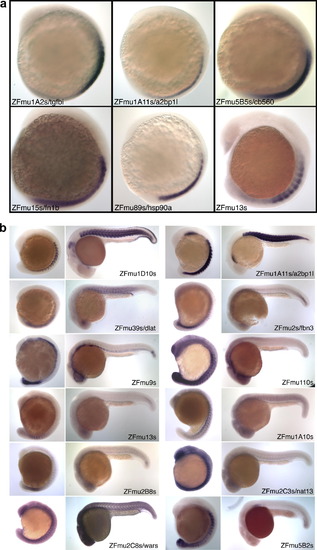
Muscle specific and novel expression patterns. (A) Whole mount in situ hybridisation (WISH) of 6 cDNAs that show muscle specific hybridisation. Lateral view of zebrafish embryos at between 3 and 9 somite stages. a2bp1l and hsp90a are also expressed in cardiac, pectoral fin and head muscles at later stages. tgfbi is dynamically expressed in the sclerotome and bone precursors later in development (Kim and Ingham, in press, and ZFIN.org:tgfbi). fn1b is a fast muscle specific fibronectin. ZFmu13s is a putative transcript that has no open reading frame, but may be a UTR for a larger gene; it is expressed in the dorsal region of the somite (Fig. 5d). Expression of ZFmu5B5s later becomes restricted to the posterior somite boundaries at 24hpf. (B) Twelve genes have expression patterns that are not described on ZFIN. The figure shows a lateral view of whole mount embryos at mid somite (10–15) and 24 hpf stages stained with each of the 12 cDNAs. With the exception of ZFmu1D10s, ZFmu5B2s and a2bp1l, the majority of these genes have a low level of expression. In addition many are expressed predominantly in the posterior forming somites and are no longer expressed after 24hpf (ZFmu13s and nat13). Most of these genes represent novel transcripts and putative transcripts. a2bp1l, dlat, nat13 and wars are listed on ZFIN, however, they have no expression data. Additional images of ZFmu1D10s, a2bp1l and dlat at later stages of development are shown in Supplementary Fig. S1. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
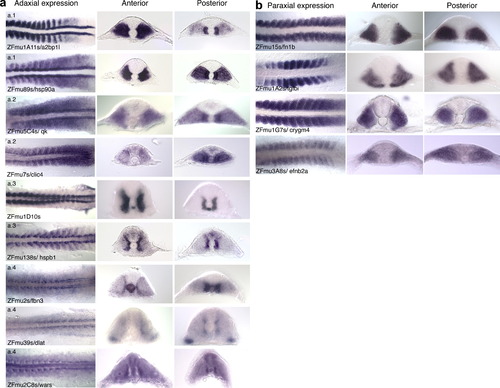
Detailed view of syn-expression patterns within the zebrafish myotome. All figures show a dorsal view of WISH stained flat-mounted embryos at 10–18 somite stages with a section taken from the anterior 5 somites and a posterior section taken within the 5 most proximal somites. Expression patterns were grouped into those with similar domains of expression. Many genes belong to more than one group. A table of the different domains of expression for each gene is shown in Table S3 in Supplementary data. (a) Adaxial expression. This includes four subgroups (a1–a4). (a.1) Those with strong expression in adaxial cells and expression in the posterior row of the somite in the paraxial mesoderm, similar to MyoD expression (a2bp1l and hsp90a). (a.2) Those with stronger expression in the posterior adaxial cells and paraxial mesoderm (qk and clic4). However, qk and clic4 differ in their expression in the paraxial mesoderm, as qk has general expression throughout the somite, whereas paraxial expression of clic4 is restricted to the anterior cells in the somite; the site of the proliferating cells that express Pax7. (a.3) Genes with expression that begins predominantly in the adaxial cells and then expands throughout the myotome as the slow muscle fibres migrate to the surface (ZFmu1D10s and hspb1). (a.4) Genes that have adaxial expression that remains medial (fbn3, dlat, wars). (b) Paraxial expression. This group is made up of adhesion, ECM and membrane proteins that are expressed in the fast muscle precursors and not in the adaxial cells. tgfbi is expressed transiently, being down-regulated in the anterior and posterior somites, whereas fn1b, crygm4 and efnb2a are expressed in all somites until 24hpf when expression in all three genes becomes restricted to the most caudal somites. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
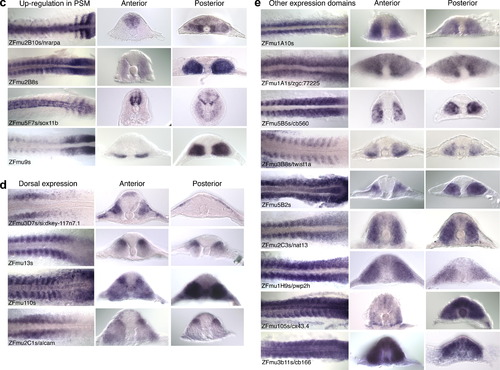
(c) Up-regulation in the presomitic mesoderm. nrarpa has oscillating bands of expression and a small region of adaxial expression in the presomitic mesoderm. ZFmu2B8s and ZFmu9s are up-regulated in the paraxial mesoderm as the new somites are formed. ZFmu2B8s is also expressed in the developing somites, whereas ZFmu9s has ventral staining in the sclerotome of the anterior somites. sox11b is expressed in the posterior somites in addition to strong neural staining. (d) Dorsal expression. This domain of expression is seen in known genes such as alcam and also 3 novel transcripts ZFmu3D7s, ZFmu13s and ZFmu110s. ZFmu3D7s is expressed in the anterior somites, whereas ZFmu13s and ZFmu110s are expressed in all somites. The expression patterns of ZFmu3D7s and ZFmu110s are very dynamic throughout development with ZFmu3D7s being expressed in a number of different tissues. e. Other domains of expression. The remaining 9 cDNAs were difficult to group. ZFmu1A10s, ZFmu1A1s, nat13 and pwp2h all have general staining in the adaxial and paraxial somite. ZFmu5B5s has a punctate expression that becomes restricted to the somite boundaries. twist1a has weak expression in the anterior row of cells in the somite, strong ventral expression in the sclerotome in the anterior somites and is also expressed in the floor plate. ZFmu5B2s is expressed strongly in the segmental plate and somites with the expression stronger around the horizontal myoseptum in the anterior somites. cx43.4 is expressed strongly in the segmental plate and towards the lateral edge of the myotome and ventrally in the sclerotome in the anterior somites. ZFmu3B11s is expressed only in the posterior half of the whole embryo, including all the somites and the lateral neural crest, while the head region has no staining. In the posterior region, there is weaker staining around the notochord. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
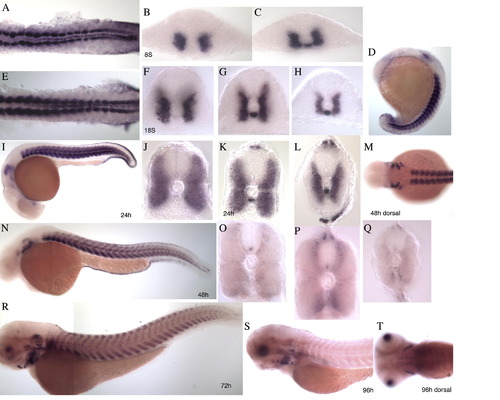
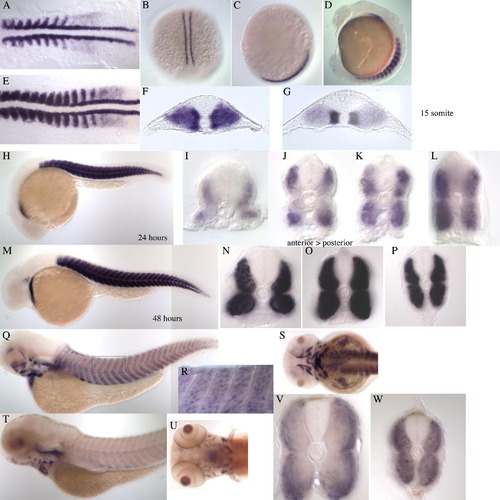
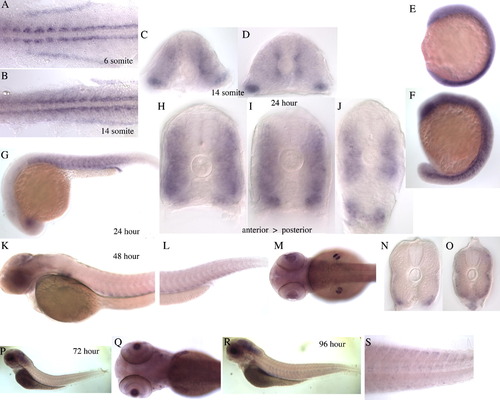
Additional in situ expression images of the transcripts, (A) ZFmu1D10s, (B) a2bp1l, (C) dlat. (A) ZFmu1D10s WISH staining of zebrafish embryos at the following stages. (A and E) Flat mounted embryos at 13 and 18 somite stages, respectively. Expression is seen in the adaxial cells and in the posterior of the hypochord. By 18 somites the expression of ZFmu1D10s in the anterior somites has expanded laterally. (B and C) Sections taken through an 8 somite embryo in the anterior (B) and posterior (C) showing expression in the adaxial cells and in the posterior hypochord, beneath the notochord in (C). (D) Lateral view of 17 somite stage embryo showing expression in the somite, hypochord and otic vesicle. F,G,H, Sections through an 18 somite embryo, anterior to posterior, showing the expansion of ZFmu1D10s expression in the most anterior somites (F) compared to the posterior section (H). The expression expands as the slow myoblasts migrate to the surface. I, 24 hpf embryo showing expression in the somite, otic vesicle, branchial arches, hypothalamus and epidermis. (J–L) Transverse sections through the 24 hpf embryo, anterior (J) to posterior (L). (M) Dorsal view of head at 48 hpf showing expression in the branchial arches and somites. N, Lateral view of 48 hpf embryo with expression in the somite, epidermis, otic vesicle and branchial arches. (O–Q) Transverse section of 48 hpf embryo, anterior to posterior. (R) 72 hpf embryo with weaker expression in the somite, stronger expression in the ear, head regions and eye. S, No expression in the somite, reduced expression in the head and eye. (T) Dorsal view of (S). (B) a2bp1l WISH staining of zebrafish embryos at the following stages (A and E). Flat mounted embryos at 8 and 15 somite stage, respectively. Expression is found in the adaxial cells and the posterior cells of the somite. (B and C) Dorsal and lateral view of a 2 somite stages embryo showing expression in the adaxial cells only. (D) Lateral view of 12 somite stage embryo showing expression in the somite and heart field. (F and G) Transverse sections of anterior (F) and posterior (G) regions of a 15 somite stage embryo showing strong expression in the adaxial cells and weaker expression throughout the lateral region of the somite. (H) 24 hpf embryo showing strong expression in the somite and heart. (I–L) Transverse sections through 24 hpf embryo, anterior through to posterior. (M) 48 hpf embryo with strong staining in the somite and heart an weaker staining appearing in the first head muscles. (N–P) Transverse sections through 48 hpf embryo. The anterior section (N) shows discrete areas of staining surrounded by areas not expressing a2bp1l. (Q) 72 hpf embryo with expression in the somite, heart and head musculature. (R) Higher magnification (40x) of the boxed region in Q showing nuclear staining. (S) Dorsal view of head region in (Q). (T) 96 hpf embryo, showing weaker expression in the somites and head muscles. (U) Dorsal view of head region in (T). (V and W) Transverse section of 96 hpf embryo, anterior and posterior, respectively, showing the central nuclear staining within the myotube. (C) 39/dlat WISH staining of zebrafish embryos at the following stages (A and B). Flat mounted embryos at the 6 somite and 14 somite stage, respectively. Stronger expression in seen in the adaxial cells and epidermis above a basal level of expression. (C and D) Transverse section through 14 somite stage embryo showing adaxial expression which is weaker by 14 somite stage. (E and F) Lateral view of 6 and 16 somite stage embryos, expression in the somites and also in the eye of the 16 somite stage embryo can be seen. (G) Lateral view of 24 hpf embryo with expression in the somite, pronephric duct and eye. (H–J) Transverse sections through 24 hpf embryo, anterior to posterior, showing expression throughout the somite, with stronger expression towards the periphery. K, 48 hpf embryo with expression in the pectoral fins, and ventral region of the somite. Weak staining is seen in the head. (L) Tailview of 48 hpf embryo. (M) Dorsal view of 48 hpf embryo. (N and O) Transverse section of 48 hpf embryo showing ventral and lateral expression. (P) 72 hpf embryo. (Q–S) 96 hpf embryo. Expression is seen in the head, eye, pectoral fins and very weakly in the somite. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|

Unillustrated author statements EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
Reprinted from Gene expression patterns : GEP, 9(2), Baxendale, S., Chen, C.K., Tang, H., Davison, C., Hateren, L.V., Croning, M.D., Humphray, S.J., Hubbard, S.J., and Ingham, P.W., Expression screening and annotation of a zebrafish myoblast cDNA library, 73-82, Copyright (2009) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Gene Expr. Patterns