- Title
-
Cloning and expression of the large zebrafish protocadherin gene, Fat
- Authors
- Down, M., Power, M., Smith, S.I., Ralston, K., Spanevello, M., Burns, G.F., and Boyd, A.W.
- Source
- Full text @ Gene Expr. Patterns
|
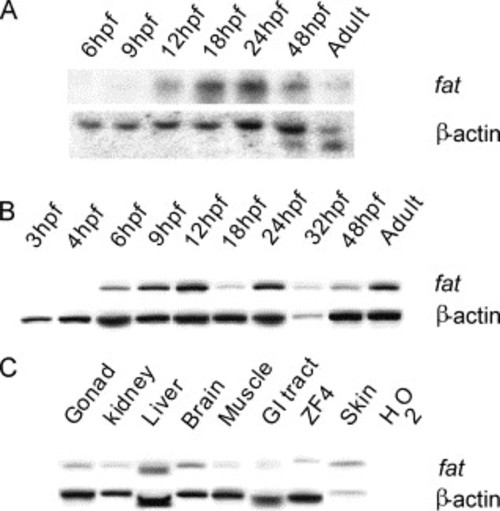
mRNA expression of fat during development and in adult tissues. Zebrafish β-actin was used as a loading control in separate reactions, on the same cDNA, and produces a 400 bp transcript. (A) Northern analysis detects a single 14 kb transcript from 12 hpf to adult. (B) RT-PCR was used to detect a 400 bp product indicating the presence of fat mRNA from 6 hpf through to adult. (C) RT-PCR detects a 400 bp fat mRNA product in most adult tissues. |
|
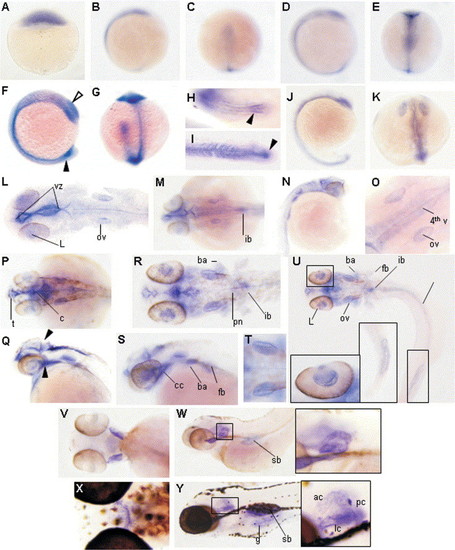
Expression of fat RNA by in situ hybridisation. A DIG labelled probe against EGFR5-FC2 of fat was used at a variety of developmental time points. (A) Expression was first seen at 4 hpf in the deep cells of the dome stage embryo, which may include the cells of the yolk syncytial layer. Expression is not then detected until after epiboly (B), (C) at 10 hpf where here is weak staining of the basal layers of the presumptive head, notochord and tail bud. With the onset of segmentation, expression is increased along the lengthening embryonic axis, and can clearly be seen in the furrow forming the notocord, head and tail structures (E). Expression is also becoming evident in the developing optic primordium, otic cup and tail bud, which is yet to extend away from the yolk (D). By 14 hpf we have strong expression throughout the embryo with the levels increasing in the optic cup, otic placode, extending tail bud, and may include Kupffer′s vesicle and the chordo-neural hinge (F), (G). The tail bud at this stage has prominent staining in the mesenchyme (arrowhead), with bilateral areas of medial somitic epithelium also staining (H). By 22 hpf only the most distal somites display expression on their posterior edge, compacting notocord mesenchyme is still strongly expressed (arrowhead) (I). At 17 hpf, staining is still present in the notochord, tail bud and head structures (J). By 22 hpf the optic primordium can be clearly seen and expression increases outlining the forming ventricles of the brain (K). (L) Represents an embryo at 26 hpf, in which the yolk has been removed and embryo flattened, a composite of 15 overlayed shots was used to capture the full depth of the embryo. Expression is now restricted to the lens of the eye (L), the otic vesicles (ov) and the lining of the ventricles from the telencephalon through to the cerebellum and 4th ventricle, encompassing the ventricular zone. Dorsally, 33 hpf expression is still prominent in the lining of the ventricles and ear and becomes apparent in the forming intestinal bulb (ib) (M). Laterally at this stage the forming fin bud is also noticeable and the notocord is still weakly positive (N). At high power it is possible to see that it is the lining of the 4th ventricle and the otic cups that are expressing (O). At 42 hpf expression persists in the lens, lining of the ventricles and otic cups, laterally the posterior tectum and the cranial cavity are outlined (arrowheads) cerebellum (c), telencephalon (t) (P), (Q). Expression at 50 hpf includes the posterior branchial arches (ba), fin bud (fb), intestinal bulb (ib), otic vesicle (ov), pronephros (p), spinal cord (sc), pronephric duct/gut (pd/g), cranial cavity (cc) and the ventricular lining. (R) Is a composite of 21 overlayed shots, inset displays staining specifically in the lining of the lens of the eye and the lining of the posterior widening gut (R), (U), and (S). Although at 50 hpf the sensory patches have formed it is the otic capsule epithelial lining that is ubiquitously expressing fat (T). By 100 hpf expression is lost in the ventricles and persists only in the brachial/gill arches swim bladder (sb) and most prominently in the sensory lining of the ear (inset) (V), (W). At 150 hpf expression is still evident in the gill arches and the sensory patches of the ear (inset) including the anterior (ac) and posterior crista (pc) and the lateral commissure (lc) but is also more evident in the lining of the swim bladder (sb) and gut (g) (X), (Y). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Expression offat RNA by in situ hybridisation. Whole mount is situ hybridised embryos were paraffin embedded and sectioned. A DIG labelled probe against EGFR5-FC2 of fat was used at a variety of developmental time points. In longitudinal cross section at 14 hpf the stained notocord cells can be clearly seen, as the main supporting structure of the embryo at this stage the cells have just started to form the characteristic open vacuoles (A). In transverse section, the large vacuoled notochord cells are stained (nc), the somites lie laterally, and the expression is restricted to the medial somitic epithelium (open arrows), and the adaxial cells, which will later develop into myotome (B). In longitudinal cross section of the posterior midbrain at 42 hpf expression can be seen in the cells lining the 4th and 3rd ventricle (v) including the ventricular zone (C). In transverse section at 50 hpf through the hindbrain, the otic capsules (oc) and the lining of the ventricle show expression (D). On longitudinal section it is only the thin epithelial lining of the lens that clearly but modestly shows weak expression of fat (E). At this same time point expression can be seen on the apical surface of cells lining the stomach (st) and the swim bladder (sb) directly ventral to the notocord (nc) (H). Later in development at 100 hpf, expression is restricted to the lining of the cranial cavity (cc) and the otic capsules (oc) (F). Posteriorly, expression can be seen on the sensory macula of the otic capsules (oc) with the lining of the 4th ventricle (v) also prominent dorsally (G). In cross section of the otic capsule at 150 hpf it is the apical surface of the macula (sm) and the processes of the sensory hair cells expressing (J). At this stage the lining of the swim bladder (sb) and the pronephric duct (pd) are expressing (I). Abbreviations: m, myelencephalon; mt, midbrain tegmentum; I, intestine. Magnification: (C), (D), (F), (G), (H) 20×, (E), (I) 40×, (A), (B), (J) 63x. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
Reprinted from Gene expression patterns : GEP, 5(4), Down, M., Power, M., Smith, S.I., Ralston, K., Spanevello, M., Burns, G.F., and Boyd, A.W., Cloning and expression of the large zebrafish protocadherin gene, Fat, 483-490, Copyright (2005) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Gene Expr. Patterns