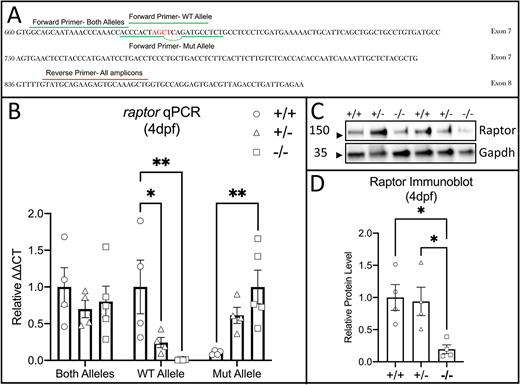
Fig. 2 Validation of the raptor mutant allele. (A) RT-qPCR primer design. Forward primer (green line) amplifying both alleles is upstream of the mutation site. Wild-type allele forward primer (broken green line) contains the nucleotides deleted in the mutant (red); the mutant allele forward primer (green line) matches the deletion. Reverse primer (red line) is in the subsequent exon (exon 8). (B) RT-qPCR using primer pairs that amplify both alleles, the wild-type (WT) allele or the mutant (Mut) allele. cDNA from 4 dpf wild-type fish (circles), 4 dpf heterozygous fish (triangles) or 4 dpf raptor mutant fish (squares) was used. No residual wild-type cDNA is detected in raptor mutants (WT Allele, squares). (C) Immunoblot with a N-terminal anti-Raptor antibody. Total protein lysates were derived from raptor wild types (+/+), heterozygotes (+/−) and mutants (−/−). This blot displays two biological replicates. The membrane was stained using anti-Gapdh antibody as a loading control. The uncropped anti-Raptor blot is shown in Fig. S3. (D) Graph of relative Raptor protein level from the heads of 4 dpf raptor wild-type (circle), heterozygous (triangle) or raptor mutant (square) fish. Raptor protein levels are significantly reduced, albeit not absent, in mutant fish. The statistical analyses were conducted using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's honest significant difference (HSD) post-hoc test for multiple comparisons, *P<0.05, **P<0.01. Data are mean±s.e.m.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Development