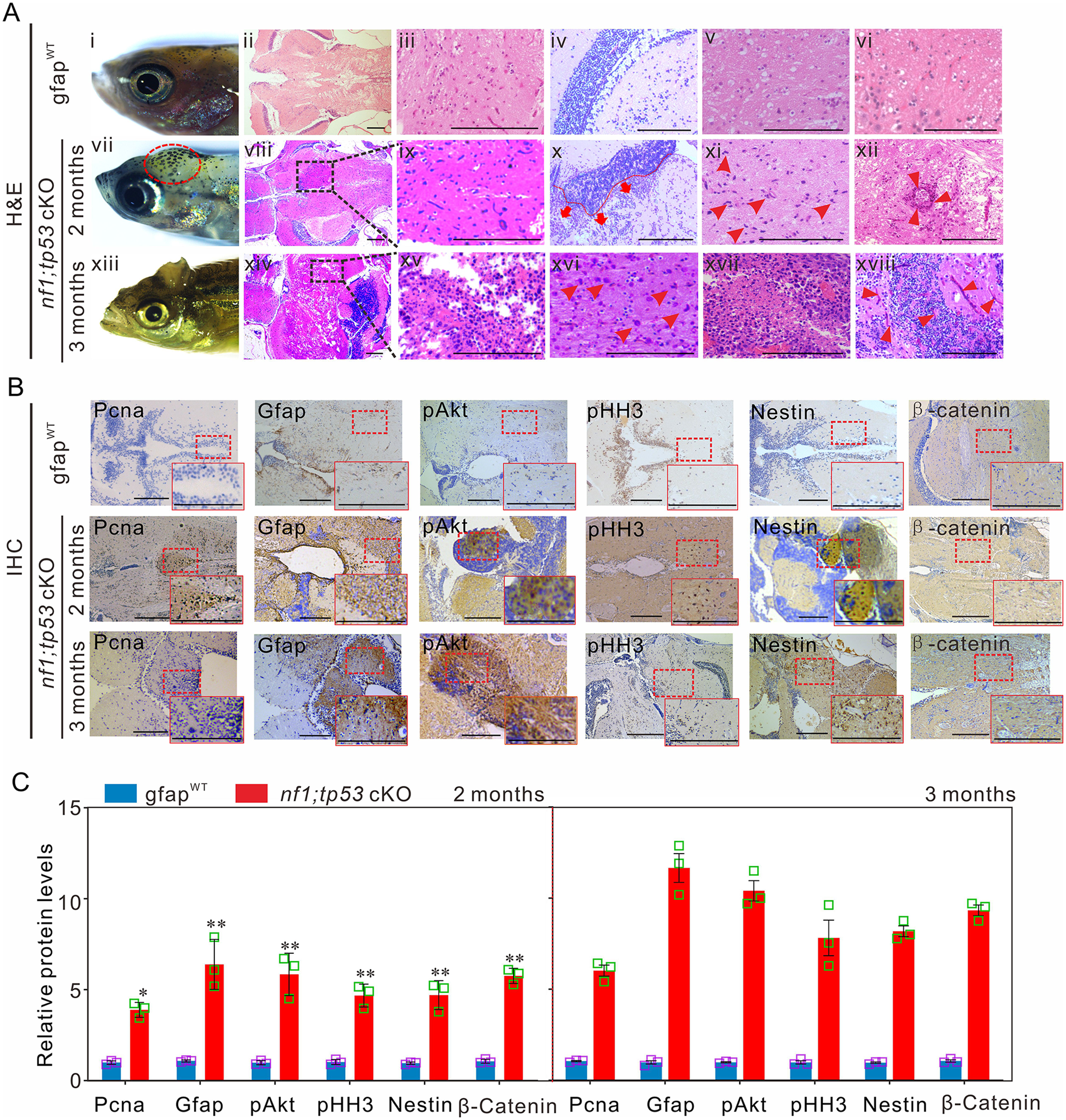
Fig. 4 Tp53 mutation promotes the development of gliomagenesis in zebrafish. (A) Histological examinations of 2-month-old gfapWT and nf1;tp53 cKO fish, and 3-month-old nf1;tp53 cKO fish. (i, vii and xiii) Representative images of the bumps on the heads of nf1;tp53 cKO fish. (ii–vi) Representative images of haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of normal brain tissues of gfapWT fish. Several typical gliomagenic phenotypes, including glioblastoma multiforme (viii and ix), increased numbers of multinucleated glial cells (arrowheads; xi and xvi), necrosis (xiv and xv), frequent vascularity (arrowheads; xii and xviii), enhanced invasive capability (red broken line; x), and the typical gliomatosis phenotype (xvii), were detected in 2- and 3-month-old nf1;tp53 cKO fish. (B) Immunohistochemistry staining was performed to examine the expression of tumour-relevant factors in brain tissues of 2-month-old gfapWT, nf1;tp53 cKO, and 3-month-old nf1;tp53 cKO fish. (C) Quantification of immunohistochemistry staining evaluated the expression of Pcna, Gfap, pAkt, pHH3, Nestin, and β-catenin in 2- or 3-month-old gfapWT and nf1;tp53 cKO fish (n = 3 for each group). Scale bars = 100 μm. Data shown as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Brain