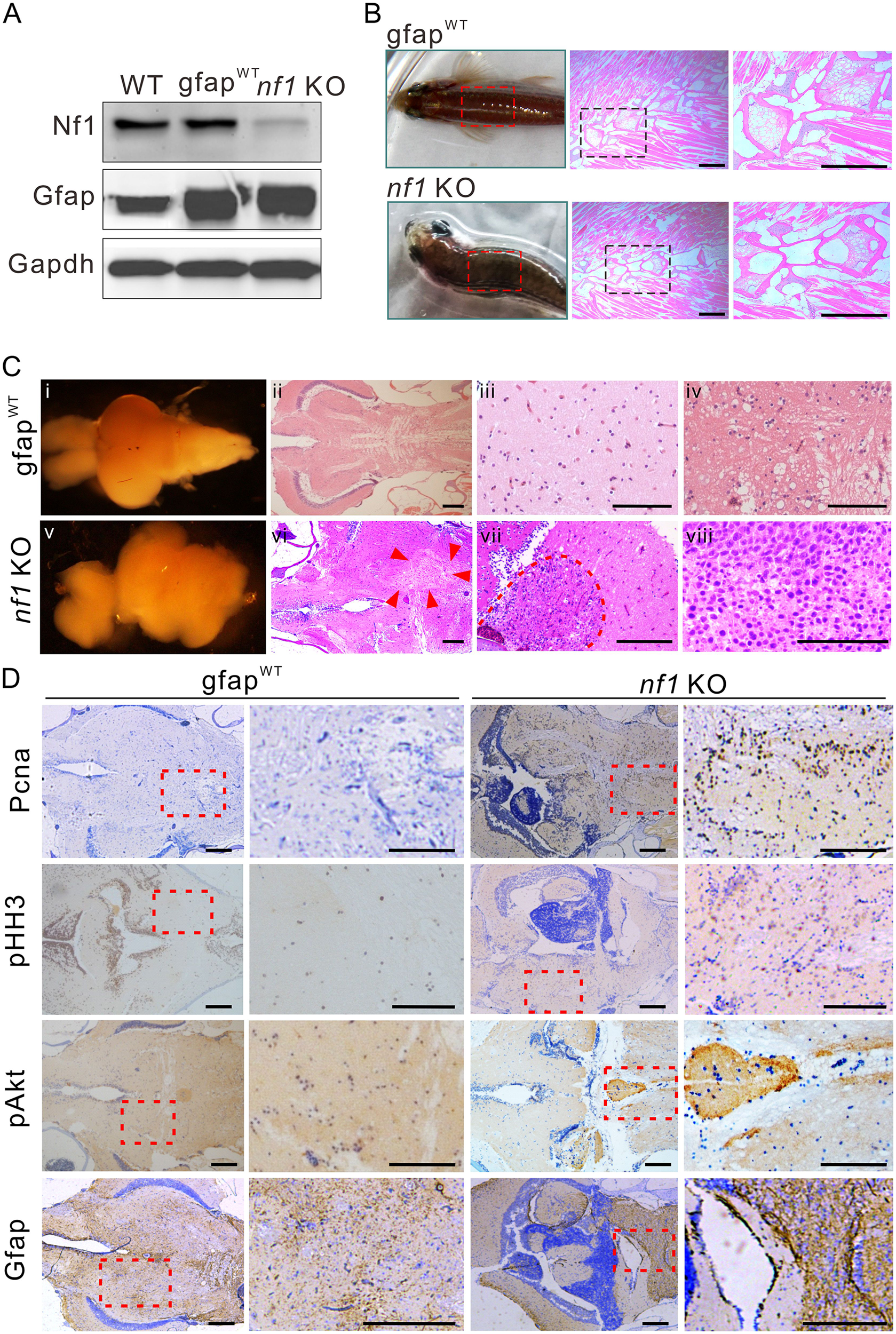
Fig. 3 Nf1 mutagenesis in radial glia disrupts the brain architecture and initiates gliomagenesis. (A) Western blot determination of Nf1 and Gfap in brain tissues from wild-type, gfapWT, and nf1 KO fish (n = 3). (B) Typical ‘bending-body’ phenotype and haematoxylin and eosin staining of spinal cord tissue in 2-month-old transgenic zebrafish. Scale bars = 50 μm. (C) The architectures and histology of brain tissues from 3-month-old gfapWT and nf1 KO fish. Brain architecture of 3-month-old gfapWT (i) and nf1 KO fish (v). (ii–iv) Haematoxylin and eosin staining of the cerebellum of gfapWT fish. (vi–viii) The tumours that formed throughout the cerebellum (at different magnifications, the boundaries were indicated by arrowheads or broken line). Scale bars = 100 μm. (D) Immunohistochemistry staining (left) and higher magnifications (right) of Pcna, pHH3, pAkt, and Gfap in brain tissues of 3-month-old gfapWT and nf1 KO fish. Scale bars = 100 μm. Data shown as mean ± SEM. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Brain