Fig. 4
Fig. 4
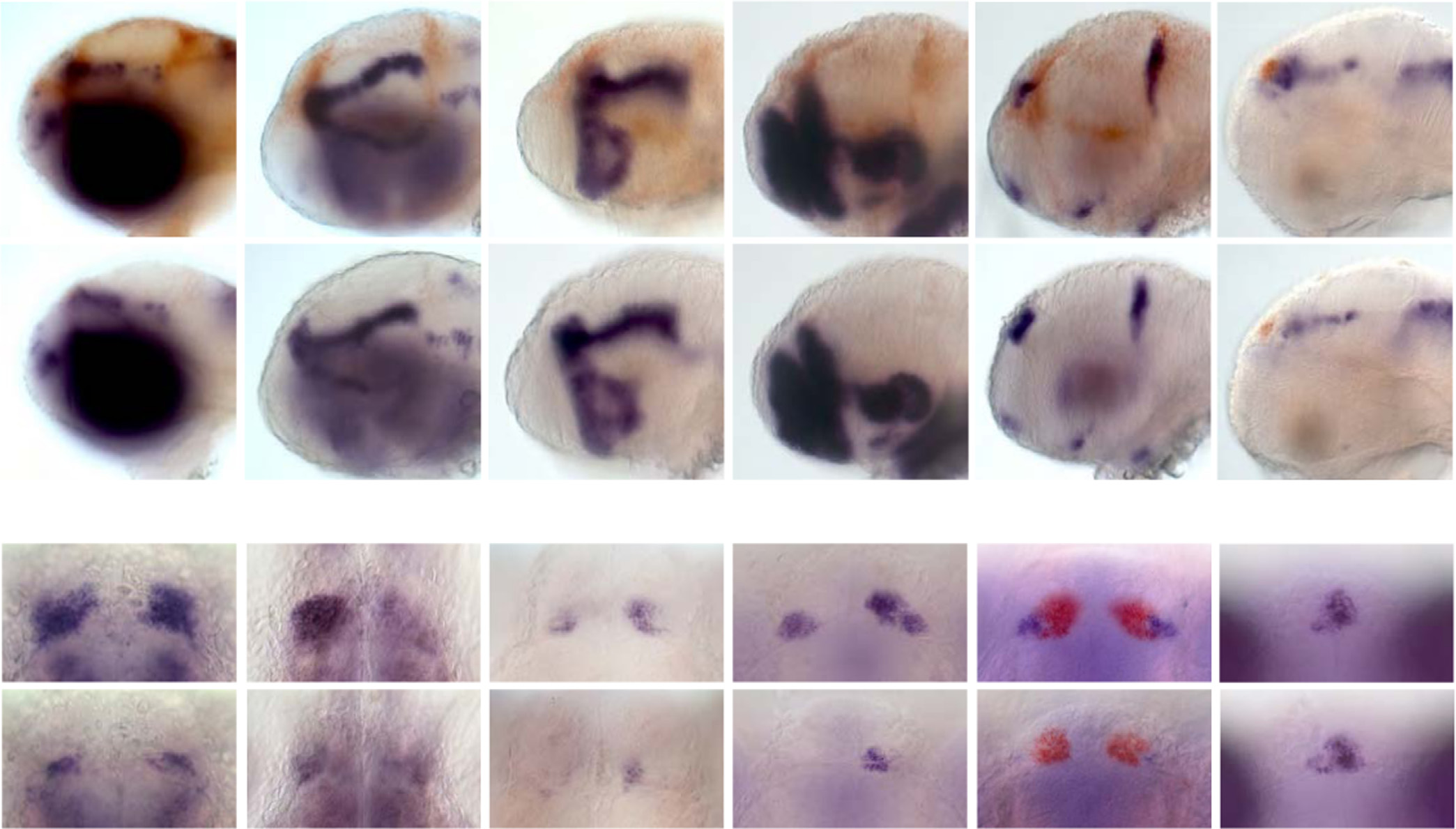
Defects in brain patterning confined to dorsal diencephalon. (A) Spatially restricted patterns of gene expression in the brains of WT and wls mutant larvae at 48 hpf. WT larvae are distinguished from homozygous wls mutants by the presence of wls transcripts (red), with the exception of kctd12.1 (red) and neurog1 double-labeling, where they are distinguished by dorsal habenular size. The neurog1 expression domain adjacent to the habenulae (arrowhead in WT) is reduced in wls mutants. (B) Gene expression in the habenular region. The dorsal habenulae of wls mutants show reduced f-spondin and ano2 expression but, despite their smaller size, L–R asymmetric gene expression (nrp1, kctd12.2, vachtb) is maintained (right dorsal nucleus indicated by arrow for vachtb). Expression of vachtb and aoc1 in the ventral habenulae (arrowheads in WT) is largely absent in wls mutants. The parapineal is positioned to the left of the pineal analage, as determined by otx5 expression, in WT and wls mutant siblings. Scale bars=100 µm. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 406(2), Kuan, Y.S., Roberson, S., Akitake, C.M., Fortuno, L., Gamse, J., Moens, C., Halpern, M.E., Distinct requirements for Wntless in habenular development, 117-28, Copyright (2015) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.