Fig. 6
The Development of VDA Region-Derived Microglia Is Independent of cMyb but Requires Runx1
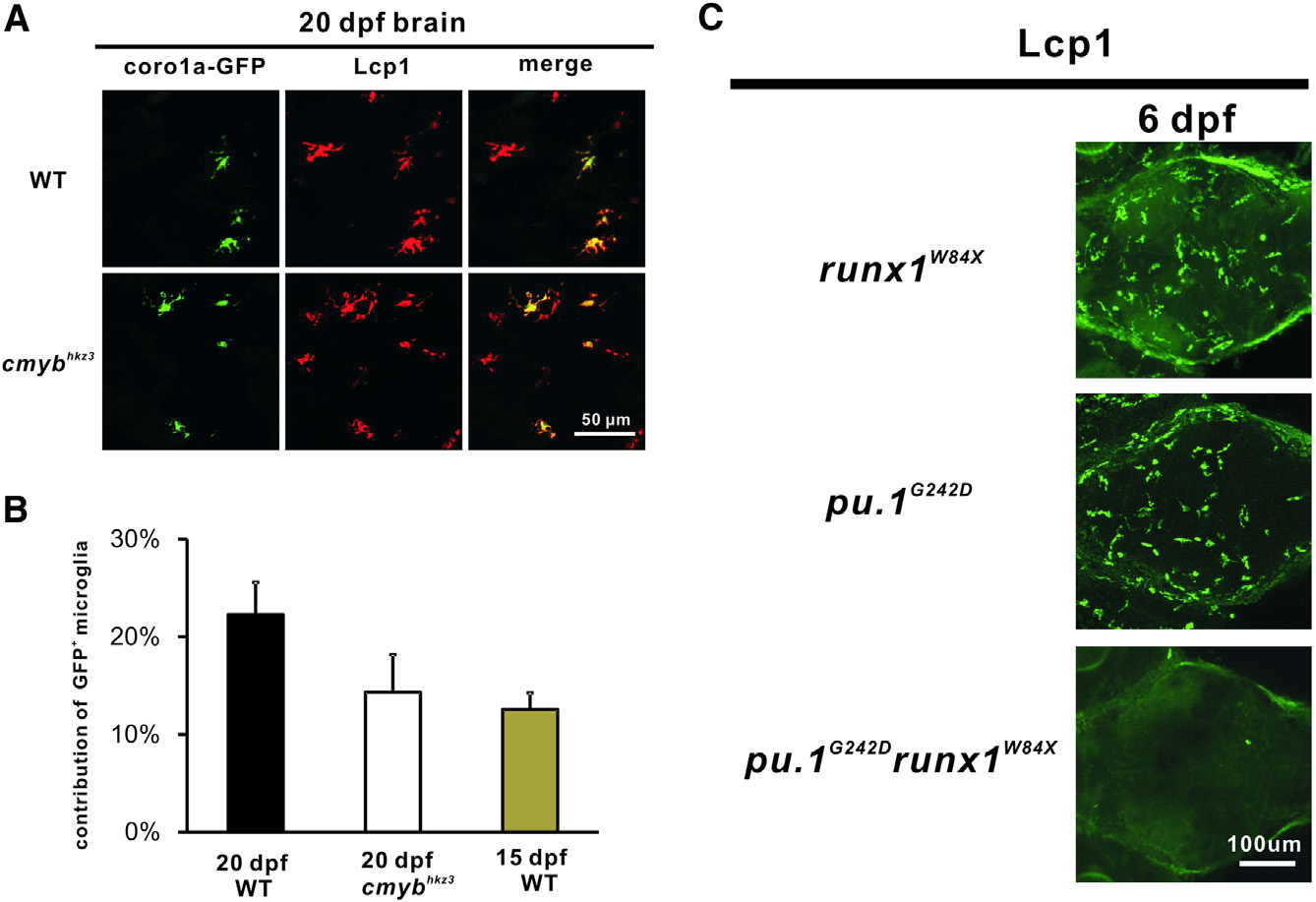
(A) The VDA-region-derived coro1a-GFP+ cells contribute to brain microglia in 20 dpf WT and cmybhkz3 mutant embryos (sectioned brain).
(B) Quantification of the contribution of the VDA-region-derived brain microglia in 20-dpf WT (n = 8), cmybhkz3 mutant (n = 8), and 15-dpf WT larvae (n = 6). Error bars represent mean ± SEM.
(C) Microglia fail to recover in the pu.1G242Drunx1W84X double mutants at 6 dpf. Stacked confocal images of immunohistochemistry staining of Lcp1 of 6 dpf runx1W84X, pu.1G242D single mutants, and pu.1G242Drunx1W84X double mutant from the dorsal view of the brain.
See also Figure S3.
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 34, Xu, J., Zhu, L., He, S., Wu, Y., Jin, W., Yu, T., Qu, J.Y., Wen, Z., Temporal-Spatial Resolution Fate Mapping Reveals Distinct Origins for Embryonic and Adult Microglia in Zebrafish, 632-641, Copyright (2015) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell