Fig. 3
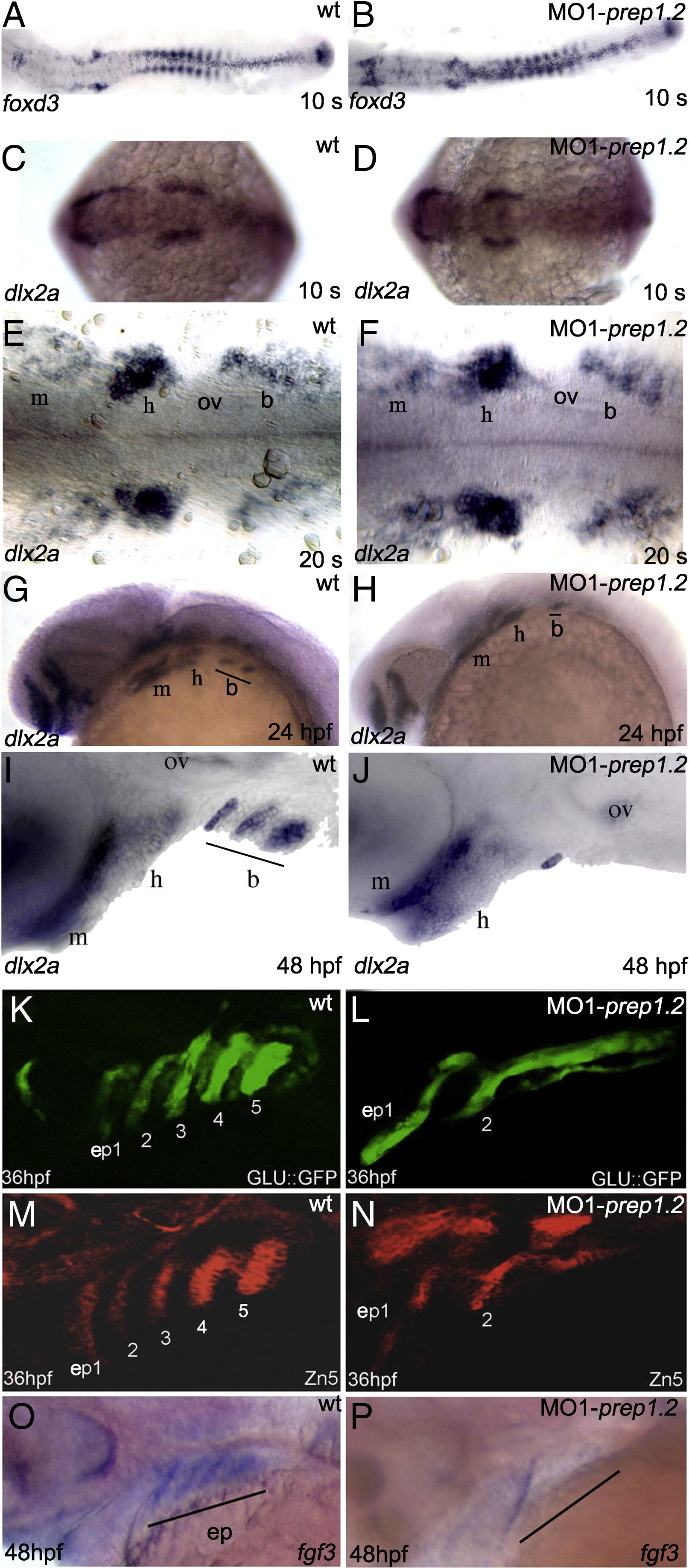
Fig. 3 Characterization of prep1.2 function. A–J: Expression pattern of pre-migratory and migratory NCC markers. A, B: prep1.2 knock-down does not affect foxd3 expression in 10 somite stage embryos (compare A and B); C–F: dlx2a expression in NCC is unaffected in prep1.2 morphants analysed at 10 and 20 somite stages; G and H: at 24 hpf expression of dlx2a is strongly downregulated in the third stream of cephalic NCC of MO1-prep1.2 injected embryos; I and J: similar results are obtained in 48 hpf embryos: in prep1.2 morphant embryos dlx2a expression disappears in posterior branchial arches (J). K–P: Failure of the posterior pharyngeal endoderm segmentation in prep1.2 morphant embryos. K–N: Analysis of pharyngeal pouches development in the glu:GFP transgenic line that express GFP ectopically in the pharyngeal endoderm and in embryos stained with Zn5 antibodies. L: in MO1-prep1.2 injected embryos analyzed at 36 hpf, the more posterior pouches (ep3–ep5) do not develop (compare with control in K). Identical results were obtained when using Zn5 antibodies to stain for the pharyngeal endoderm (compare N with control in M, see also Supplemental Fig. 5). O and P; lack of fgf3 expression in the pharyngeal endoderm of prep1.2 morphants (F). A–F: dorsal view; G–P lateral view. b: branchial arches; ep: endodermal pouches; h: hyoid cartilage; m: Meckel′s cartilage; ov: otic vesicle.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 343(1-2), Vaccari, E., Deflorian, G., Bernardi, E., Pauls, S., Tiso, N., Bortolussi, M., and Argenton, F., prep1.2 and aldh1a2 participate to a positive loop required for branchial arches development in zebrafish, 94-103, Copyright (2010) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.