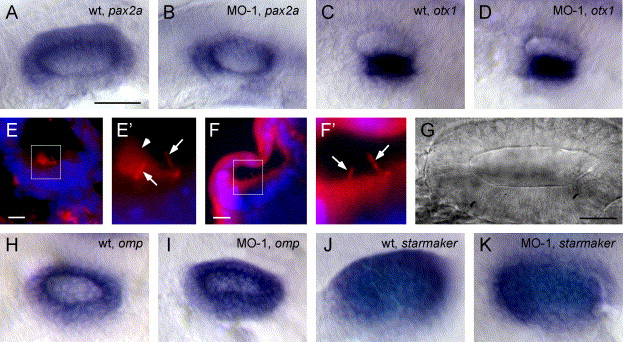
Fig. 3 Normal gene expression and otocyst morphogenesis in morphants. (A) The pax2a expression in wild-type and (B) morphant otocyst. (C) otx1 expression in a wild-type and (D) morphant otocyst. (E) Immunohistochemistry for acetylated tubulin on 10 μm frozen sections through a 28 hpf wild-type otocyst. Tether cell kinocilia (arrow) and otolith (arrowhead) are evident in magnified insert (E′). (F) Morphant otocyst examined for acetylated tubulin. Tether cell kinocilia are evident in magnified insert (F′) (arrow) but no otolith seeding particles were present. (G) DIC image of the otocyst of a morphant fish (100×) at 24 hpf. No aggregated matrix was visible in several ears examined in this manner. (H) omp expression in wild-type and (I) morphant otocyst. (J) starmaker expression in wild-type and (K) morphant otocyst. A–D and H–K are whole mount in situ hybridizations of 24 hpf embryos. All otop1 morphant fish were injected with 4 ng MO-1 at the one-cell stage. Rostral is on the left. Scale bars: A–D, H–K, 250 μm; E–F, 10 μm; G, 25 μm.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 276(2), Hughes, I., Blasiole, B., Huss, D., Warchol, M.E., Rath, N.P., Hurle, B., Ignatova, E., David Dickman, J., Thalmann, R., Levenson, R., and Ornitz, D.M., Otopetrin 1 is required for otolith formation in the zebrafish Danio rerio, 391-402, Copyright (2004) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.