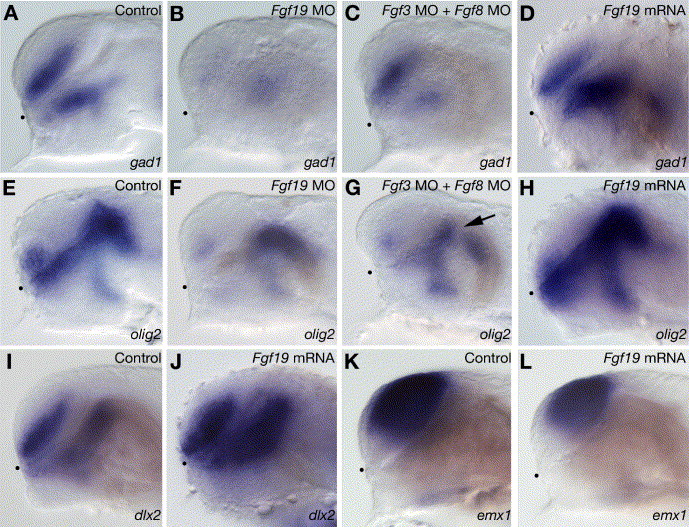
Fig. 8 Specification of GABAergic interneurons and oligodendrocytes. (A–D) gad1 expression in wild-type embryos (A) and embryos injected with Fgf19 MO (B), Fgf3 MO and Fgf8 MO (C) or Fgf19 mRNA (D) at 28 hpf. (B) The injection of Fgf19 MO resulted in a severe reduction of gad1 expression in both the ventral telencephalon and nTPOC. (C) In the embryos injected with both Fgf3 MO and Fgf8 MO, gad1 expression in the nTPOC was severely reduced, while that in the ventral telencephalon decreased slightly. (D) The injection of Fgf19 mRNA resulted in increased expression of gad1 in the forebrain. (E–H) olig2 expression in wild-type embryos (E) and embryos injected with Fgf19 MO (F), Fgf3 MO and Fgf8 MO (G) or Fgf19 mRNA (H) at 28 hpf. (F) In the embryos injected with Fgf19 MO, olig2 expression in the dorsal thalamus was unaffected, while that in the subpallial telencephalon and ventral thalamus decreased significantly. (G) In the embryos injected with both Fgf3 MO and Fgf8 MO, olig2 expression in the subpallial telencephalon, anterior ventral thalamus and zli (arrow) was reduced, while that in the posterior ventral thalamus and dorsal thalamus was unaffected. (H) In the embryos injected with Fgf19 mRNA, olig2 expression in the forebrain increased significantly. (I and J) dlx2 expression in wild-type embryos (I) and embryos injected with Fgf19 mRNA (J) at 26 hpf. (J) The injection of Fgf19 mRNA resulted in increased expression of dlx2 in the telencephalon and diencephalon. (K and L) emx1 expression in wild-type embryos (K) and embryos injected with Fgf19 mRNA (L) at 26 hpf. (L) The injection of Fgf19 mRNA resulted in decreased expression of emx1 in the telencephalon. Lateral views with anterior to the left and dorsal to the top. Dots indicate the boundary between the telencephalon and ventral diencephalon.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 288(1), Miyake, A., Nakayama, Y., Konishi, M., and Itoh, N., Fgf19 regulated by Hh signaling is required for zebrafish forebrain development, 259-275, Copyright (2005) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.