Fig. 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-240614-15
- Publication
- Ding et al., 2024 - Klebsiella pneumoniae alters zebrafish circadian rhythm via inflammatory pathways and is dependent on light cues
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
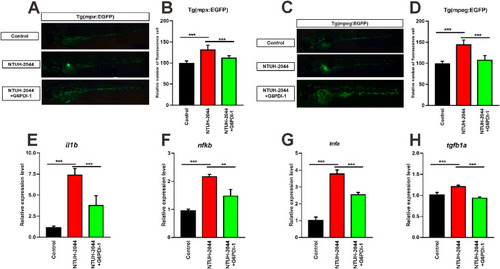
Anti-inflammatory drugs reduce Klebsiella pneumoniae-induced inflammation. Zebrafish were infected with NTUH-K2044 for 48 hpf, followed by treatment with the anti-inflammatory drug G6PDi-1, and inflammation was evaluated at 5 days post-fertilization (dpf). (A) Neutrophil recruitment in Tg(mpx:EGFP) transgenic zebrafish in the control, NTUH-2044, and NTUH-2044+G6PDi-1 treatment groups. (B) Number of neutrophils in Tg(mpx:EGFP) transgenic zebrafish in the control, NTUH-2044, and NTUH-2044+G6PDi-1 treatment groups. (C) Macrophage recruitment of Tg(mpx:EGFP) transgenic zebrafish in the control, NTUH-2044, and NTUH-2044+G6PDi-1 treatment groups. (D) Number of macrophages in Tg(mpx:EGFP) transgenic zebrafish in the control, NTUH-2044, and NTUH-2044+G6PDi-1 treatment groups. qRT-PCR analysis of inflammation-related genes il1b (E), nfkb (F), tnfα (G), and tgfb1a (H) in the control, NTUH-2044, and NTUH-2044+G6PDi-1 treatment groups. Each experiment was performed in triplicate. Data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). Data were analyzed by Student's t-test.(ANOVA) (**P < 0.01,***P < 0.001). |