Fig. 3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-230915-3
- Publication
- Patterson et al., 2023 - Abrogation of MAP4K4 protein function causes congenital anomalies in humans and zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
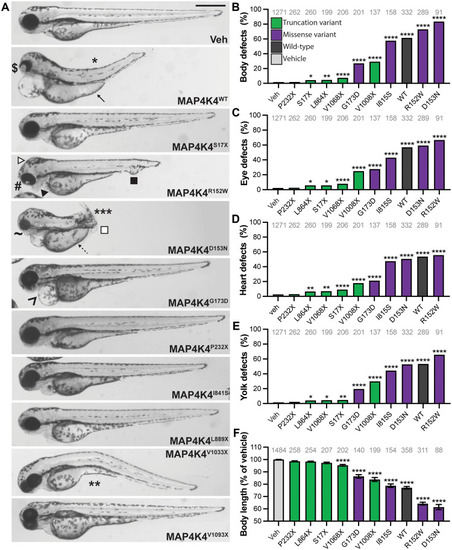
MAP4K4 variants cause LOF.
(A) Larvae microinjected with variant MAP4K4 were imaged at 3 days post fertilization (dpf); representative lateral views are shown. Ectopic expression of MAP4K4 caused developmental defects, including craniofacial anomalies (CFAs; closed arrowhead), hydrocephaly (white arrowhead), and cloacal defects (closed square). Larvae are arranged according to the position of the variant within the protein (top to bottom; N to C terminus). (B to E) Developmental defects were quantified as a percentage of total larvae displaying the defect. (B) Body defects included dorsal (*), ventral (**) and lateral (***) curvatures, and truncations (white square). (C) Eye defects included coloboma ($), cyclopia (#), and small eyes (~). (D) Heart defects included pericardial edema (^). (E) Yolk defects included thickening of the yolk extension (solid arrow) and absent yolk constriction (dashed arrow). (F) Body length was measured and normalized to the average of the vehicle-injected siblings (Veh) and is reduced by expression of MAP4K4WT and missense variants but is less affected by truncation variants. Scale bar, 500 μm (A). Graphs (B to F): pale gray, vehicle; dark gray, MAP4K4WT; purple, missense variants; and green, truncation variants. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001 by pairwise chi-square test (B to E) or Student’s t test (F) compared to vehicle. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) gives P < 0.0001 for (F). n numbers are inset to graphs in gray text. Error bars represent SEM. WT, wild type. |