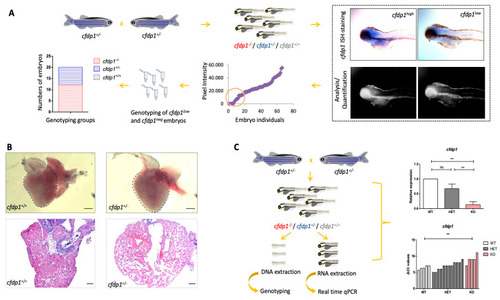
Study of cfdp1−/+ embryonic and adult hearts. (A) Expression of cfdp1 in cfdp1 siblings (pool of three genotypes: cfdp1−/−, cfdp1−/+, cfdp1+/+). After performing in situ hybridization using the cfdp1 RNA probe in cfdp1 siblings (n = 69) at 120 hpf, ISH signal intensity was quantified. The cfdp1low and cfdp1neg ISH signal embryos were genotyped (n = 20) and it was confirmed that they corresponded to cfdp1−/− and cfdp1+/- embryos. (B) Brightfield images of freshly isolated whole-mount hearts (upper panels) and brightfield images of 5 μm paraffin-embedded, H&E-stained cardiac slices (lower panels) of 7 months post fertilization (mpf) cfdp1+/+ (n = 3) and cfdp1+/- (n = 3) adult hearts. Scale bar (upper panels): 200 μm; scale bar (lower panels): 50 μm. (C) Workflow strategy. Collection of cfdp1 siblings after cross of heterozygous cfdp1 adult fish followed by RNA isolation and genotyping of single embryos. As shown via quantitative real-time PCR, cfdp1 expression levels in cfdp1−/− embryos are statistically significantly reduced compared to the wild-type cfdp1+/+ siblings when normalized to act2b as a reference gene. (C) cfdp1+/- embryos exhibit a range of gene expression (ΔCts plot) while a portion of heterozygous embryos present similar expression levels to the mutant embryo siblings. Student’s t-test (two-tailed distribution, unpaired); ** significantly different p-value < 0.01; ns: non-significant. Data are presented as mean ± SD.
|

