Figure 4—figure supplement 2.
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-230707-67
- Publication
- Chen et al., 2023 - Defining function of wild-type and three patient specific TP53 mutations in a zebrafish model of embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma
- Other Figures
-
- Figure 1
- Figure 1— supplement 1.
- Figure 1— supplement 2.
- Figure 2.
- Figure 3
- Figure 3—figure supplement 1.
- Figure 3—figure supplement 2.
- Figure 3—figure supplement 3.
- Figure 3—figure supplement 4.
- Figure 4
- Figure 4—figure supplement 1.
- Figure 4—figure supplement 2.
- Figure 4—figure supplement 3.
- Figure 5
- Figure 5—figure supplement 1.
- Figure 5—figure supplement 2.
- Figure 5—figure supplement 3.
- Figure 5—figure supplement 4.
- Figure 6
- Figure 6—figure supplement 1.
- Figure 6—figure supplement 2.
- Figure 6—figure supplement 3.
- Figure 6—figure supplement 4.
- Figure 7
- Figure 7—figure supplement 1.
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
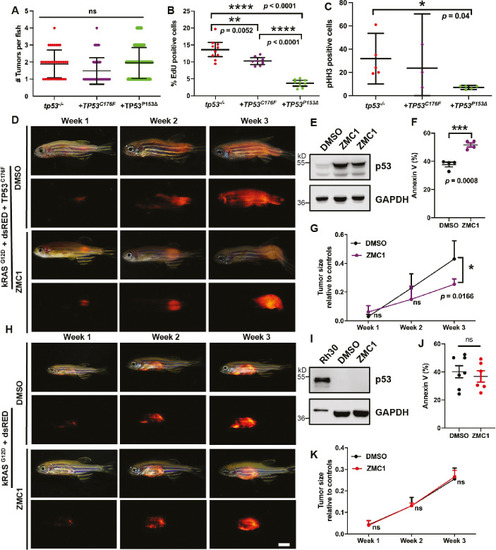
Assigning pathogenicity to two human TP53 sarcoma mutations in the kRASG12D-driven embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma (ERMS) model. ( |