Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-230707-47
- Publication
- Zhang et al., 2023 - Wdr5-mediated H3K4me3 coordinately regulates cell differentiation, proliferation termination, and survival in digestive organogenesis
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
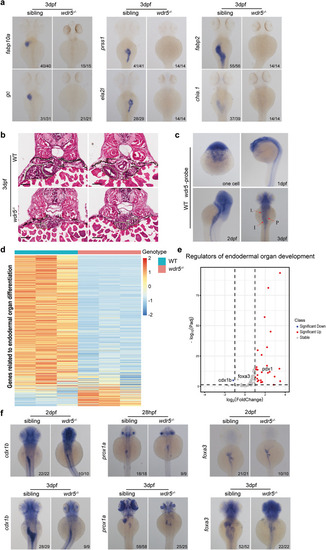
The differentiation of intestine, liver, and exocrine-pancreas is impaired in |