Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-230112-1
- Publication
- Anderson et al., 2021 - Tbx5a and Tbx5b paralogues act in combination to control separate vectors of migration in the fin field of zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
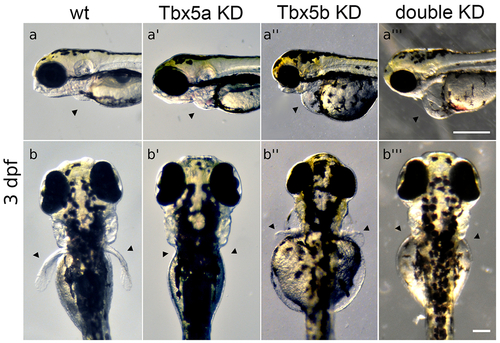
Tbx5 knock-down embryos display heart and pectoral fin defects. (a-a’’’) Arrowheads point to position of heart. Views are lateral with anterior to the left. Scale bar=250μm. (a) Normal wt heart development. (a’) Tbx5a-knock-down embryos display edema and defects in heart looping. (a’’) Tbx5b-knock-down embryos display edema and defects in heart looping. (a’’’) Double knock-down embryos have linear hearts and edema, (b-b’’’) Arrowheads point to normal position of pectoral fins. Views are from dorsal aspect with anterior to the top. Scale bar=100μm. (b) Wt embryo showing both fins at 3 days post-fertilization (dpf). (b’) Tbx5a knock-down embryos lack pectoral fins, (b’’) Tbx5b knock-down embryos display small, misshapen fins. (b’’’) Tbx5a/Tbx5b double knock-down embryos do not form pectoral fins. Panels a, a’’, b and b’’ reproduced from Boyle Anderson and Ho (2018). |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 481, Boyle-Anderson, E.A.T, Mao, Q., Ho, R.K., Tbx5a and Tbx5b paralogues act in combination to control separate vectors of migration in the fin field of zebrafish, 201-214, Copyright (2021) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.