|
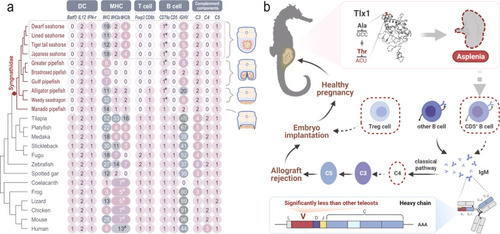
Immunogenomic basis of asplenia and male pregnancy in seahorses. Immunogenomic basis of asplenia and male pregnancy in seahorses.a Copy numbers of key genes involved in the development and function of DC, MHC, T/B lymphocytes, and complement components 3–4 in seahorses and other vertebrates. DC dendritic cell, MHC major histocompatibility complex. *, variation of ITAM (immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif) region; †, based on partial sequence (low-coverage sequencing and genome assemblies), but featuring the variation of ITAM; #, Total number of MHC II. The brood pouch types are shown on the right. Hippocampus and Syngnathus species exhibit the closed brood pouches. b Schematic map illustrating the hypothesized molecular trade-offs in the male pregnancy of seahorses. Asplenia caused by the tlx1 mutation could decrease the CD5+ B cell populations. In addition to the corresponding reduced diversity in antibodies, the classical complement pathway triggered by antibody-antigen-interactions might also be weakened, affecting the downstream events usually triggering allograft rejection. Loss of C4 is expected to be associated with decreased abundance of Treg cells, which orchestrate self-immune tolerance. The shaded icon and dotted line indicate gene loss in seahorse genomes. Treg cell, regulatory T cell. The figures were created with BioRender.com.
|