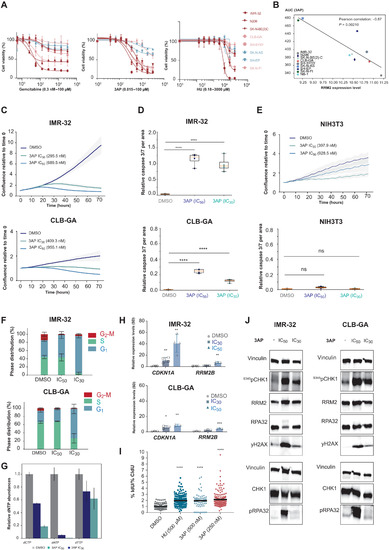
Fig. 4. Comparative RNR inhibitor analysis to kill neuroblastoma cells. (A) 3AP treatment can establish lower half-maximal inhibitory concentrations than gemcitabine and HU in a panel of neuroblastoma cell lines, with MYCN-amplified cell lines and the nonamplified CLB-GA cell line being more sensitive than MYCN-nonamplified cell lines (red: MYCN amplified, adrenergic; orange: MYCN nonamplified, adrenergic; blue: MYCN nonamplified, mesenchymal). (B) 3AP sensitivity (AUC) is negatively correlated to RRM2 mRNA expression levels in a panel of neuroblastoma cell lines. (C) Treatment of IMR-32 and CLB-GA neuroblastoma cells with 3AP at their respective half-maximal inhibitory concentration significantly reduces cell confluence and (D) induces cell death. (E) Nonmalignant murine NIH3T3 fibroblasts did not show reduced confluence or apoptosis induction upon 3AP exposure. (F) IC30 values for IMR-32 and CLB-GA neuroblastoma cells impose a significant S phase cell cycle arrest. (G) Endogenous dNTP pools are reduced upon exposure of IMR-32 neuroblastoma cells to 3AP. (H) 3AP (IC50) treatment leads to a significant increased CDKN1A and RRM2B expression. (I) DNA combing following exposure of IMR-32 neuroblastoma cells to HU or 3AP shows a significant increased levels of stalled forks upon 3AP treatment versus controls. IdU, 5′-iododeoxyuridine. (J) Immunoblotting for DNA damage response markers (pRPA32 and yH2A) and CHK1/S345pCHK1 in protein extracts of neuroblastoma cells treated with fixed IC30 and IC50 of 3AP (for quantification, see fig. S2). CIdU, 5-chloro-2’-deoxyuridine.
|